Money laundering isn't just a financial crime; it's a global issue that siphons off an estimated $800 billion to $2 trillion annually, according to the United Nations. This staggering figure represents about 2-5% of the world's GDP, highlighting the importance of understanding how this illicit process works. But how does dirty money make its way into the legitimate financial system? It happens through a well-structured method involving three distinct stages. First, let's learn the meaning of money laundering.
What is Money Laundering?
Money laundering is an illegal act in which large amounts of money are used to conduct criminal activities in drug trafficking, terrorism, or any other corruption. It is a threat to the global financial system and a serious risk to market integrity. This article is a guide that highlights the three stages of money laundering which are placement, layering, and lastly integration.
What Are the 3 Stages of Money Laundering?
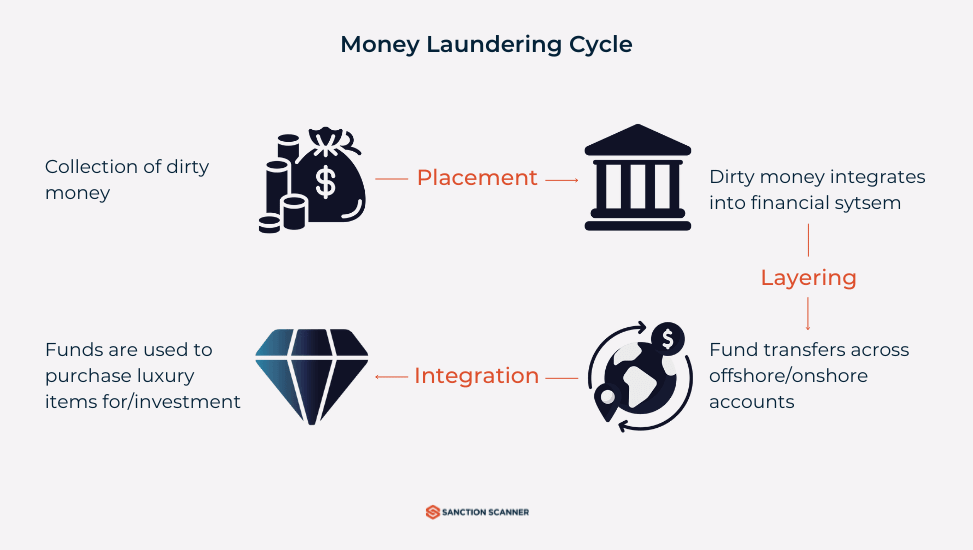
Money laundering is the act that enables criminals to camouflage money that originates from a dirty, illegal 'Source A' so that it looks like it came from a clean, legal 'Source Z'. There are three stages of money laundering. In the first stage, placement, unlawfully acquired funds are incorporated into the legal economy. The second stage, layering, entails criminals obscuring the origins of illicit funds by redistributing them through various means. The third stage, integration, occurs when the illicit funds, now disguised as legal currency, are extracted and put to use.
Both local and international organizations make an effort in by using economic and legislative means to prevent suspicious activities for money laundering and supervise related institutions. Almost every country has a national anti-money laundering (AML) compliance system according to its risks and local dynamics. In the international area, there are regional and global authorities. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is one of the most efficient actors in this field.
The money laundering process generally unfolds in three distinct stages aimed at legitimizing illicitly obtained funds within the legal financial system. These three phases are as follows:
- Placement
- Layering
- Integration
The Global Impact of Money Laundering
- Distorts markets, fuels inflation, and creates economic imbalances, particularly in developing countries.
- Causes loss of revenue, reputational damage, and exposes businesses to multimillion-dollar fines or license suspension by regulators.
- Funds organized crime, terrorism, and corruption, weakening global security and governance.
- Slows economic growth by diverting resources from essential public services, increasing inequality, and widening the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Money laundering perpetuates corruption, further destabilizing economies and undermining the trust of foreign investors.
What Are the AML Regulations and Legal Frameworks?
AML strategies are effective if they strictly follow international and national regulatory frameworks. Here is a guide to regulatory highlights for financial institutions and their compliance obligations:
FATF Recommendations: When combating money laundering and financing terrorism, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) arranges internationally recognized standards. Recommendation 10 (Customer Due Diligence) verifies customer identities and monitors their transactions. In addition, Recommendation 20 (Suspicious Transaction Reporting) reports any suspicious activity. FATF Recommendations are fundamental in maintaining transparency within the financial system.
EU 6AMLD: Building upon FATF Recommendations, the European Union’s 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) strengthens the legal framework. It is a directive that introduces a list of 22 offences, including cybercrime and environmental crime. EU 6AMLD will prove to be a liability for companies across EU member states.
U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA): It is required by the U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) that financial institutions must implement monitoring systems for suspicious activities. Institutions must file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) and Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs) under the supervision of FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network).
Why Is It Important to Combat Money Laundering?
Tackling money laundering is vital for a multitude of reasons, and here's why:
- Maintains market integrity and reduces inflation risks.
- Protects institutions from fines and reputational damage.
- Disrupts financing for terrorism, drug trafficking, and human trafficking.
- Promotes accountability and reveals corrupt activities.
- Ensures a level playing field and ethical operations.
- Channels resources into public services and infrastructure.
- Builds confidence among investors and global partners.
How To Prevent Money Laundering?
- Implement strong anti-money laundering policies and procedures.
- Perform Customer Due Diligence (CDD) to verify identities and assess crime involvement before service use.
- Apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for customers deemed higher risk.
- Conduct ongoing monitoring to review transactions and detect suspicious behavior.
- Utilize transaction monitoring software to identify unusual patterns and scrutinize dubious transfers.
- Carry out independent AML audits to find and address deficiencies in your practices.
How Does the Sanction Scanner Help?
Sanction Scanner provides a comprehensive solution to combat financial crime with customer screening, customer risk assessment, transaction monitoring, and fraud detection. Our technology ensures your business remains compliant with the latest AML regulations while effectively detecting suspicious activities. Experience how Sanction Scanner can enhance your AML strategies by requesting a demo today.



