What Is AML/KYC Compliance for Payment Service Providers?
You should think of payment service providers as the most important detail of modern payments. With options like payment processors, e-wallet platforms, or fintech startups, these providers are used a lot. These companies operate in risky environments where suspicious activities can occur; so, having anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) is more than another rule your company should comply with.
What Are AML Payment Processors?
Payment service providers that have embedded AML controls are known as AML payment processors. Rather than just providing transactions, these processors monitory transactions in areas like credit cards, bank transfers, and cryptocurrency to make sure no red flag goes unnoticed. AML payment processors are tasked with monitoring users and taking note of any odd activity they notice according to FATF standards. Some processors also don’t stop at this but also offer systems for submitting STRs.
Key Characteristics of AML-Compliant Payment Processors
These processors are tasked with many requirements they need to follow. Let’s talk more about the features of AML-compliant payment processors that help achieve these requirements. Firstly, KYC/KYB checks are provided by the processor to verify customers and companies your firm comes in contact with. Another feature is sanctions and politically exposed persons (PEPs) screenings against OFAC, the UN, and the EU watchlists; these help prevent suspicious people from ever interacting with your company.
AML-compliant payment processors also use transaction monitoring which is important for every company that has a big volume of transactions. Risk scoring is provided to companies; this is done to divide customers to risk categories which help with giving adequate attention to high-risk customers. Finally, automated suspicious transaction reporting (STR) is among the features these processors offer. Detecting and reporting odd activities should be priority number one for your company, getting this service in an automated manner speeds up the process.
Who Needs AML Payment Processors?
Several industries deal with regulatory requirements that signal companies to implement compliance solutions to help them. For example, crypto firms should be careful with anonymity risks since these firms are newer, work in a digitalised environment and anonymity can be achieved because of these reasons. These companies should comply with the FATF’s Travel Rule as well; so, to reach the required transparency the regulations want, reaching compliance and using these processors is important.
Online gambling platforms should be detecting layering schemes that are done to hide fraud and meet strict licensing requirements that prove they are in compliance. Fintech apps are in need of these processors because they operate in a sector where there is a high volume of transactions in a fast manner. High risk industries like forex trading, adult entertainment, and online gaming are under strict regulatory requirements and they can benefit from embedded AML solutions.
Finally, global marketplaces that are operating international transactions need to manage sanctions exposure accordingly and get help from AML payment processors. According to Statista.com's estimates, people will lose $343 billion to online payment fraud between 2023 and 2027. These numbers should encourage you towards compliance.
Why AML/KYC Compliance Is Essential for Payment Services?
Now, let’s talk more about why AML/KYC compliance is needed for payment providers. These providers are working with huge transaction volumes; so, this is a risky environment suitable for illicit funds to go unnoticed. Payment providers that operate globally also need to comply with AML/KYC regulations since the nature of global transactions can create regulatory gaps and different legal standards across different countries can make it more difficult to regulate.
PSPs are different from regular banks where they don’t verify customers in real life, face-to-face. The inability to provide face-to-face verification makes it harder for PSPs to prevent identity fraud. So, what risks can you face for non-compliance? Hopefully, our readers are taking the needed precautions to reach AML/KYC compliance. But, for those who aren’t, fines that can go up to hundreds of millions of dollars. Another risk is license recovation since your operations aren’t safe. Finally, the reputational damage you may face can be deadly for your company.
Key AML/KYC Requirements for Payment Service Providers
The first feature is customer due diligence (CDD). CDD requires collecting and verifying identification details to make sure the customer actually exists. Finding out the purpose of account is another step that needs to be taken. After getting these essential information, ongoing monitoring is really helpful to make sure no risks occur.
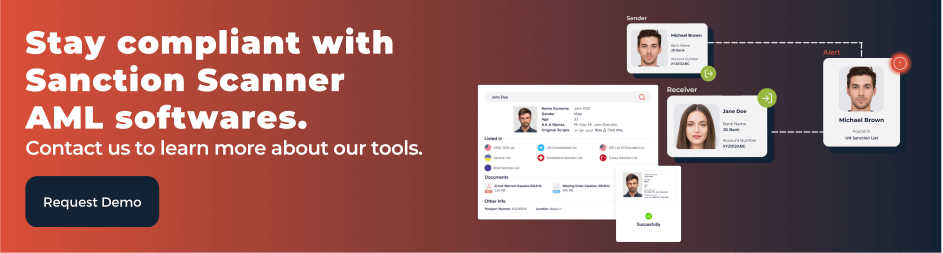
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is another feature. This requirement is needed especially for politically exposed persons (PEPs). Our readers need to make sure the high risk clients are throughly watched. Offshore entities are another part that need to be watched closely. Verifying the origin of these companies’ and PEPs’ funds is needed. Transaction monitoring is also needed. Transaction monitoring provides solutions to detect structured transfers that are meant to hide the origin of the money. Real time analytics given by this feature is helpful for catching risky activities. Sanctions and PEP screening is one other feature that helps. This feature is helped by OFAC, UN, and EU sanctions lists. Ongoing checks are needed to regulate accordingly.
You should be fulfilling your reporting obligations to meet your requirements. Filing suspicious activity reports (SARs) when odd transactions occur is needed. Maintaining records for audits also helps immensely.
Major Global Regulatory Bodies and Frameworks Governing AML/KYC
FATF is the first regulatory body you should follow; with their 40 recommendations, they are the foundation of AML regulations. In the EU, the Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) deals with company compliance and penalties for non-compliance.
In the US, Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is needed for collecting and analysing financial data to figure out if odd activities are occurring. Fenergo’s report reveals critical insights into the regulatory landscape. According to Fenergo, nearly 50 fines were issued by U.S. regulators in 2024, with North America accounting for an overwhelming 95% of the $4.6 billion in global financial penalties. In the UK, Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is the main regulatory body; while in Australia, AUSTRAC is the responsible body for different industries.
Finally, Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is the regulatory body for Singapore; it helps companies reach AML requirements.
What Are the Challenges in AML/KYC Compliance in Payment Services?
Of course, AML/KYC compliance is not reached without challenges, the same goes for payment services as well. The first challenge faced is complex ownership structures; these layered structures and offshore firms make it harder to detect the ultimate beneficial owner (UBO). Another problem that you may face is synthetic identity fraud; this is where criminals create profiles with real information they stole and fake information they lie about.
One other challenge is providing frictionless onboarding without giving up AML compliance requirements. You should want to provide a fast and problem-free onboarding process without risking non-compliance. Also, evolving regulations that are continuously updated where audits are needed may be another challenge payment services face.
Best Practices for Ensuring AML/KYC Compliance
Here are some advice for our readers who wish to reach AML/KYC compliance. A good starting point for you is implementing a risk-based approach; this approach will help you divide customers according to their risk levels, which will ensure you pay more attention to high-risk customers more easily. Using advanced technology like AI powered tools can make the process of detecting odd activities easier.
Employee training can ease your anxiety about AML/KYC compliance, since training your team will help recognise red flags and know how to escalate suspicions to alerts. Finally, internal audits that are done regularly will make sure all the precautions you took previously are working as intended and there are no gaps in your systems.
How Sanction Scanner Facilitates Seamless Compliance
Our Sanction Scanner is here to help your company reach AML/KYC compliance. With our real-time screening feature, sanctions, PEP screenings and adverse media screenings are made easier; having continuous monitoring of your customers is a great step to take. Our team provides customisable reports in case you find odd activity within transactions you are monitoring. Our API integration helps you with embedding features in PSP ecosystems. Another feature we provide is the risk engine, which can tailor the rules you need to comply with according to your company.
The Vixio Payments Compliance Outlook reveals that 90% of compliance teams feel overwhelmed on a monthly basis regarding payments compliance. Help your team by partnering with Sanction Scanner.
FAQ's Blog Post
Payment companies need AML/KYC to prevent financial crime and meet global regulatory standards.
Payment providers check customer identity, address, and risk level before onboarding.
Payment companies face risks like money laundering, fraud, and sanctions violations.
Large, cross-border, or unusual transactions require enhanced AML checks.
Payment firms should update customer data regularly and trigger reviews based on risk.
AML software with screening, monitoring, and reporting helps payment companies stay compliant.
Sanction Scanner offers real-time screening, risk-based monitoring, and audit-friendly reporting in one platform.