In this blog post, we’ll talk about how Know Your Customer (KYC) measures implement themselves into the crypto sector as a whole. KYC involves verifying customers before they can start using your service. KYC measures also help reduce crypto fraud daily. Crypto firms benefit from this since the measures aim to create a safer platform with anti money laundering (AML) and counter terrorist financing (CTF) compliance.
How KYC Works in the Crypto?
KYC essentially asks for checking people’s identification details during different stages of a partnership with your company. Another regulation KYC brings is asking companies to be careful with large transactions and make checks accordingly. Since it is another KYC recommendation, companies monitor fiat to crypto conversions; your company should be careful and monitor accordingly when cash is exchanged for digital assets, this step is important for spotting red flags. The final KYC recommendation is implementing an identity validation system to support you during the verification stages. Biometric checks and encrypted databases can help immensely.
The spread of digital wallets held on platforms like Coinbase Global is attracting hackers, most recently to obtain client data; exchange hacks rose 17% last year, according to compliance firm TRM.
What Are KYC Requirements for Crypto Exchanges?
There are several KYC requirements designed specifically for crypto firms and we’d like to inform our readers more about it all. The first action to take is identity verification where the firm needs to check identification details against official information. Similar to this, address verification is also required. Customers can verify their address details by providing a utility bill, a bank statement that’s recent, or another form of proof to ensure they are real.
Biometric verification is a newer solution for companies to add extra security by asking for a selfie or live video from the customer. Liveness detection and facial recognition technology similarly helps ensure that the person is real and not providing false information. Sanctions and politically exposed person (PEP) screening is also required to ensure compliance. These screenings make sure your customers are checked against international watchlists by FATF and OFAC to flag customers that are high-risk.
Ongoing monitoring is the next step after all these processes make onboarding safer and more efficient. Customers should be monitored to catch in case they show suspicious behaviour. High-risk individuals may also need to give details about their source of wealth to ensure enhanced due diligence (EDD) compliance.
Global KYC Compliance in Crypto
KYC compliance regulations change by different jurisdictions and your company should also adapt accordingly. Crypto firms and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) should be in compliance with AML regulations regardless of their location. We’ll be checking out how these regulations are shaped in different regions. In the U.S. the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) asks crypto companies to register as Money Services Businesses (MSBs) to then further implement KYC to ensure AML compliance. Next, in the EU, the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) along with the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) are working together to bring compliance to crypto companies. The UK has the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) to enforce AML laws by asking for SAR filings, CDD, and more. In Singapore, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) deals with VASP registration and further imposing KYC and transaction monitoring requirements.
In Japan, Financail Services Agency (FSA) is there to enforce KYC under the Payment Services Act (PSA). Sometimes, regulatory bodies from different jurisdictions work together to ensure compliance. The May 2024 theft from Japan-based crypto firm DMM involving $308m worth of assets was carried out by a North Korean threat group tracked as TraderTraitor; this information was unveiled by the collaboration of US and Japanese authorities.
In India, the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU-IND) wants companies reporting under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA). One other example is Australia with AUSTRAC; this regulatory body is there to require KYC compliance for Digital Currency Exchanges (DCEs). Meanwhile in Canada, FINTRAC is the responsible regulatory body to regulate as a part of its virtual dealer framework. In South Korea, KoFIU is there to require real-name banks accounts to be linked to crypto accounts, making it one of the strictest regulatory bodies.
What Are KYC Regulators by Country (Crypto Sector)?
| Country | Regulator |
| USA | FinCEN |
| EU | ESAs / AMLA |
| UK | FCA |
| Singapore | MAS |
| Japan | FSA |
| India | FIU-IND |
| Australia | AUSTRAC |
| Canada | FINTRAC |
| UAE | VARA / CBUAE |
| Hong Kong | SFC |
| Thailand | SEC Thailand |
| Malaysia | SC Malaysia |
| Brazil | CVM / Receita Federal |
| South Africa | FSCA |
| Türkiye | MASAK |
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) enforces VASP registration just like Singapore, and it does so via Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA). Hong Kong, on the other hand, has Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) deals with crypto firms by requiring full licensing from them. Thailand has its Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to mandate biometric checks while making a new account. Malaysia is setting rules for digital currency exchanges (DCEs) by its Securities Commission (SC).
Latin America and Africa companies are also dealing with compliance requirements. In Brazil, Receita Federal asks companies for KYC data submission and transaction reporting; in South Africa, the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) is there to check companies’ AML compliance. Our final example is Türkiye, which is the world’s fourth-largest cryptocurrency market. The Financial Crimes Inverstigation Board (MASAK) is requiring VASP registration and KYC implementation to ensure compliance as a whole.
How KYC Affects the Use of Crypto Wallets
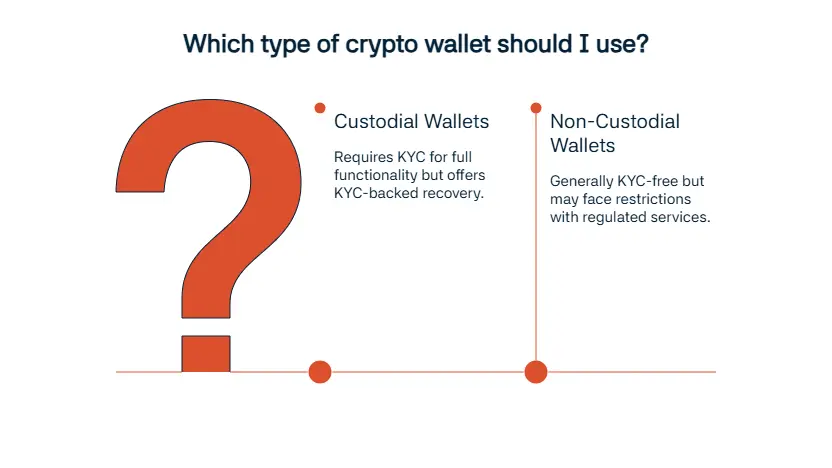
KYC first affects the use of custodial and non-custodial wallets. With custodial wallets, KYC is always required before users can get to fully access the wallet; centralized exchanges offer these. The customer should submit identification documents, biometric checks, and proof of address to ensure KYC; without these, customers often get banned from making withdrawals or transactions of any kind. Non-custodial wallets like MetaMask, Trust Wallet and Ledger are often operating without KYC requirements. With these, users can control their own private keys to freely complete transactions. But, since identity checks are not done, some other examples have started to emerge in the DeFi sector; some are starting to experiment with KYC measures to help regulators. Non-custodial wallets are not fully anonymous, though. These wallet’s addresses can be tagged and linked to a user when they use a KYC-verified company, and blockchain analytics are used to complete this action. Identity clustering and transaction tracking are useful when companies and especially regulators want to map out the wallet activity and match it to a real person.
Transaction limits are also affected. Firms have a divided system to make sure partial KYC only gets you small transactions, whereas full KYC gets you higher limits for all. KYC also affects wallet security and recovery. Wallets of custodial kind offer a service of ID-based recovery methods to use when their customer loses access, the same can’t be said for non-custodial wallets. These wallets are only saveable with the private key the customer possesses.
KYC vs. eKYC in Crypto
Both of these measures were put in place to ensure a person’s identity is verified, but, of course, they have their differences. KYC works by submitting real-life identity documents like a passport, driver’s license, or utility bill of the person to then get checked manually by a compliance officer. This process is long, taking from 24 to 72 hours, especially if it’s a big firm. It is an effective way of ensuring compliance and preventing fraud, but our readers will agree that it is a slow processes that may be filled with more obstacles since it involves physical documents and manual labor.
Electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) is the speedy alternative to traditional KYC. People are allowed to upload their IDs digitally with this measure. Optical character recognition (OCR) is there for firms to use during the validation process of documents. Biometric verification also helps by offering options like selfies, live video, and faical recognition. Since there is no physical document or manual control involved, your customers can complete their verification in even under five minutes. Fraud is reduced and prevented by features of eKYC like liveness detection and AI based facial matching. Our Sanction Scanner team recommends using eKYC will help your company onboard more people faster and in a more efficient way.
Challenges of Implementing KYC in Crypto
Let’s talk more about the difficulties of conducting KYC checks in a sector like crypto. Crypto has often been singled out for money laundering and illicit purposes by pro-banking politicians such as the ranking member of the Senate Banking Committee, Senator Elizabeth Warren. But there are more challenges that you may face while implementing KYC.
The first hurdle your company may face is that the KYC measures’ conflict with decentralization. Crypto sells the idea of anonymous and peer-to-peer interaction, but KYC measures are trying to achieve the exact opposite by demanding official documents from customers. Another problem is data privacy risks. You may be required to give sensitive information of yours to crypto firms, which in turn makes them extra vulnerable against hackers and data breaches of every kind. Firms should be able to find a way that ensures security while also not giving up on compliance. Alena Vranova, founder of SatoshiLabs, has reported in 2025 an increase in physical attacks on cryptocurrency holders caused by data breaches.
We’ve mentioned above how each jurisdiction has different regulatory bodies they respond to and different laws accordingly. Keeping track of these facts in a relatively new sector like crypto is challenging. AML and KYC rules must be checked according to that specific region to avoid fines and ensure compliance. Finally, crypto experience of speedy and accessible transations may get interrupted by KYC measures. Every user needs to sign up and verify themselves with official documents, which creates a longer process than some would like. eKYC speeds things up a fair amount, but this is still an issue our readers should pay attention to.
Benefits of Crypto KYC (for Exchanges & Users)
We’ll talk about the good side of using KYC measures for crypto, thinking of both our readers who own their own company and those who are just users of crypto platforms. 92% of centralized crypto exchanges globally are KYC-compliant in 2025 (up from 85% in 2024). For crypto platforms, these measures are a safe and sure way of ensuring legal compliance and avoiding fines. These checks reduce fraud by implementing verification and scaring scammers away. These KYC measures can be integrated with payment service providers (PSPs) and banks. Crypto being a newer and less regulated sector makes it harder to convince banks to work with them, but these KYC programs are one way to ensure banks that your company is safe to work with. Your company’s reputation will benefit greatly from implementing KYC measures to earn trust from both traditional entities like banks and customers alike. Our Sanction Scanner experts say that 57% of crypto users report improved trust and transparency in firms that adhere strictly to KYC regulations. Chainalysis also reports that all crime types have decreased in value in recent years, the importance of KYC for more transparent blockchain technology is highlighted by their report.
If you’re just using crypto platforms, having a safer space to trade should make you feel better about signing up to that specific platform. KYC measures reduces scams, identity theft, and market manipulation. Having a verified account is a sure way to prove your crypto asset ownership, these help with tax and legal clarity while filing taxes and being ready for potential legal disputes. KYC compliance will often mean higher transaction limits and access to premium features for you. Some of these are faster withdrawal options, margin trading, and fiat on-ramps.
FATF Travel Rule and Its Impact on Crypto KYC
The Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) Travel Rule is there to create a transparent environment for payments. The Travel Rule requires VASPs to be in compliance with global standards by enforcing sender and recipient details to be kept and shared with regulators when needed just like traditional banks. The Travel Rule also has a data sharing obligation, and this obligation helps regulators catch and trace odd activity. The obligation helps reduce the amount of money laundering and terrorist financing going on in the crypto platforms.
Penalties for KYC Non-Compliance in Crypto
Crypto firms that aren’t complying with KYC requirements may face lots of penalties, starting from financial penalties. These fines can add up to millions, or even billions in the most crucial cases. Other than that, your company may face license suspensions, your operations may get restricted, your company may even get shut down. The executives of your company may face personal liability, criminal charges are possible for deliberate financial cases. Finally, most importantly, your company will face reputational damage since you’re involved with financial crimes, leading to reduced trust. In 2020, CB Payments Limited (CBPL), part of the Coinbase Group, was fined £3.5 million after it continued onboarding over 13,000 “high-risk” users despite a voluntary agreement not to do so. Our Sanction Scanner experts report that in 2024, KYC deficiencies were responsible for 31% of all penalties in the crypto sector, contributing to a total of $1.25 billion in fines, a 35% increase over 2023.
KYC in Centralized vs. Decentralized Platforms
A centralized exchange (CEX) and a decentralized exchange (DEX) operate differently when it comes to AML compliance. Binance and Coinbase can be given as examples for centralized platforms; these more often than not require KYC measures. These firms are custodians, holding your funds and being the one responsible for regulations. These companies are tasked with implementing strong AML and KYC measures to ensure compliance.
Decentralized platforms are mainly not using KYC when operating, Uniswap and PancakeSwap can be given as examples. You as a user are responsible for your own assets in this case. There are no central authorities to hold your funds for you in this option; so, KYC measures are not mandatory. This might change since regulators are asking for more from DEXs in terms of compliance. KYC-free casinos are growing in popularity since those who want to gamble using crypto are looking for platforms who are not verifying their identities. These developments show that KYC compliance in decentralized platforms might be a bigger issue in the next few years.
FAQ's Blog Post
KYC (Know Your Customer) in crypto refers to the process of verifying the identity of users on cryptocurrency platforms to prevent money laundering and fraud.
KYC helps crypto exchanges comply with AML regulations, detect suspicious activity, and build trust with regulators and users by verifying customer identities.
Most regulated crypto exchanges and wallet providers, such as Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken, require users to complete KYC before trading or withdrawing.
Commonly required documents include a government-issued photo ID (passport or driver’s license), proof of address (utility bill), and sometimes a selfie.
Not always. KYC is mandatory on regulated platforms, but some decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and wallets may allow limited access without identity checks.
Yes, small purchases may be possible without KYC on peer-to-peer platforms or DEXs, but most reputable exchanges require identity verification.
Yes, KYC reduces anonymity by collecting and storing user data, which may concern privacy-focused users, but increases security and regulatory compliance.
Reputable exchanges use encryption and secure storage to protect KYC data, but users should still choose trusted platforms to reduce the risk of data breaches.





