What Is Transaction Monitoring?
Transaction Monitoring is a kind of real time screening of financial transactions. The purpose is identifying the potential money laundering and other activities that can be led to fraud. It detects & identify any kind of suspicious activity to maintain AML compliance and protect your business. Implementing Transaction Monitoring eliminates numerous Anti Money Laundering risks when applied correctly. In this post, we will go over everything related to this process in detail.
Why Should Firms Use AML Transaction Monitoring?
1. Compliance
First and foremost, Transaction Monitoring is an obligation. Several authorities such as FATF, FinCEN and EU AMLD, have their own requirements and expect firms to comply. Also, transaction monitoring alone is not enough to stay compliant, there are other obligations you must keep in mind such as reporting Suspicious Activity Reports. Let’s give an example from recent times. According to Yahoo Finance, AUSTRAC, Australia’s financial intelligence agency, ordered the Australian arm of Binance to appoint an independent auditor due to vulnerabilities in its crime prevention systems. Among the reasons they have mentioned, it is possible to see ineffective transaction monitoring as well.
2. Financial Crime Risk
It is always better to tackle any problem before they even escalate, and this is particularly one of the reasons why Transaction Monitoring plays such an important role in AML efforts.
3. Risk-Based Customer Management
Most of the authorities also expect firms to update customer risk profiles in real-time. Another advantage of this is that you can allocate your resources accordingly and not waste any time.
4. Regulatory Fines
Ineffective, or absent Transaction Monitoring has several repercussions. You may face severe financial penalties and sanctions. This may even reach a point where your business’s operating licence is revoked.
5. Supporting Audits
Several monitoring systems can maintain comprehensive audit trails. This proves very helpful for the times you need to file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
6. Fraud Prevention
They can also directly help your business prevent fraud since it detects any anomaly that comes up. For example, using AML transaction monitoring software, credit card and point-of-sale (POS) device activities are tracked and analysed. These acts help uncover fraudulent activities. Also, machine learning algorithms are used. These help identify unusual behavior and flag suspicious transactions. This in turn ensures the improvement of fraud detection.

Who Needs AML Transaction Monitoring?
1. Banks & Credit Institutions
Banks and credit institutions are definitely one of the first institutions that come to mind, since they handle high-volume transactions each day. Also, the strictest regulations are usually imposed on these. For example, The German financial authority, BaFin, has requested Deutsche Bank to improve its transaction monitoring.
2. Fintechs & PSPs (Payment Service Providers)
These are definitely faster when it comes to transactions. The speed of these microtransactions through API-based platforms creates one of the ideal environments for fraudsters committing financial crimes.
3. Crypto Exchanges & VASPs (Virtual Asset Service Providers)
Similar to Fintechs and Payment Service Providers, Crypto Exchanges and Virtual Asset Service Providers work in a dynamic and constantly changing landscape. These institutions must conduct proper wallet tracing and comply with FATF Travel Rule as well.
4. Gambling Platforms
There is no doubt that these platforms witness high cash turnovers but they also allow online anonymity. Thus, fraudsters can easily exploit these for the placement and layering of funds.
5. DNFBPs (Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions)
If you are wondering what Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions are, we can exemplify these with real estate agents, lawyers, accountants and high-value goods dealers. So, it is basically the same case with previous sectors, which is taking part in complex and large transactions.
6. MSBs (Money Service Businesses)
MSBs encompass remittance companies, currency exchanges and prepaid card providers. We consider these high-risk due to cash intensity and cross-border movement of funds. So, pretty similar to the previous examples.
7. Wealth Management
Our last example is once again concerned with managing complex investment portfolios, as you may have been expecting. These can get very vulnerable to misuse, since they may be hiding beneficial ownership or moving illicit wealth.
Why Is Transaction Monitoring So Important, Especially for Banks?
In AML solutions, a single reason is often enough to justify the need for applying a solution. However, Transaction Monitoring presents us many advantages from adhering to laws to protecting your reputation.
Let’s start with regulatory compliance. There are countless laws such as FATF standards, EU AML Directives, FinCEN rules or even local regulations, which require firms to adhere to strict monitoring processes and file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
One obvious reason is that monitoring helps detect fraud. There is an account takeover? Monitoring could address that. Someone committed trade-based laundering? Monitoring will let you know that. Since it detects fraud early, it can prevent a lot of financial and reputational damage beforehand. For example, criminal groups laundered more than $670 million through TD Bank accounts. According to authorities, this was due to the fact that they didn’t monitor 92% of the bank’s transactions, which resulted in $3 billion in penalties.
It also proves very helpful regarding Customer Risk Management, because a proper Transaction Monitoring system can spot behavior changes and apply Enhanced Due Diligence. For example, a customer that you consider low-risk may make a high-value international transfer, which can seem very unusual. Transaction Monitoring can update their risk accordingly without any manual intervention.
Last but not least, staying away from fraud is the best possible way you can protect your reputation and this is exactly what Transaction Monitoring can help you with. Even the slightest failure can damage your reputation, which could take years to recover. So, Transaction Monitoring can both prevent these failures and show the customers that you are serious about AML compliance.
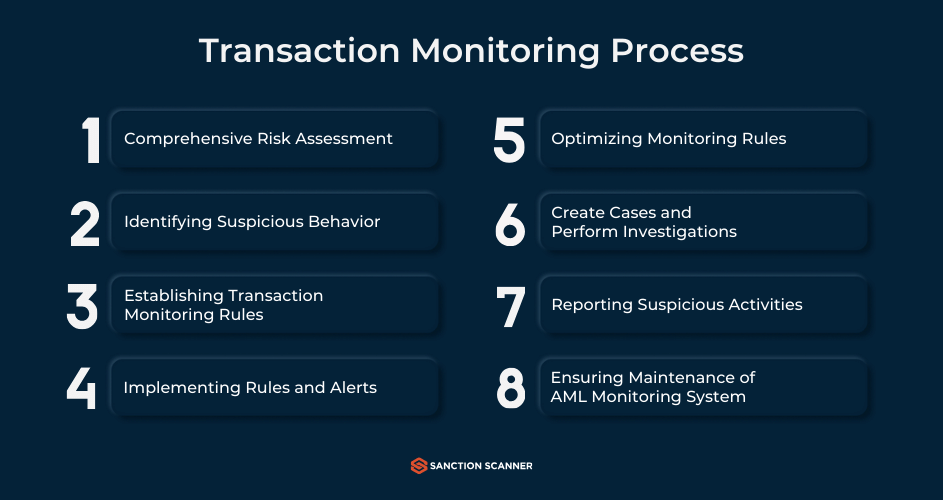
How AML Transaction Monitoring Works
In this part, we will explain how Transaction Monitoring works, step by step. First, the system gathers all details of transaction data (amount, frequency, geolocation, counterparties etc.) and Know Your Customer information (customer identity, risk rating, source of funds etc.). Now, the part where predefined rules and thresholds are applied. Firms are starting to use more and more machine learning in this part because they can identify anomalies more efficiently such as structuring, rapid movement of funds or transactions with high-risk jurisdictions. The next step consists of alert generation. When monitoring system identifies an activity that matches suspicious patterns, it triggers an alert and prioritizes based on risk severity. The alarms can be arranged to your company’s liking, including different thresholds, high risk countries and their currencies can be added. This part mostly concerns compliance teams. They must investigate alerts, review customer profiles and decide whether activity is legitimate or suspicious. If they indeed find an activity suspicious, they must file a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with the relevant authority. Now, the only thing left to do is keeping the relevant reports (activities, alerts, investigations etc.) for at least 5 years due to the regulatory requirements and future audits.
What is AML Transaction Monitoring Software?
AML Transaction Monitoring Software is basically a tool that analyzes financial data to detect any suspicious activity while ensuring adherence to AML regulations at the same time. The software helps you by scanning large amounts of financial transaction data. Bank transfers, credit card payments, and other financial activities analysed thanks to the feature. The most important information are ones like sender, receiver, amount, location, date and time, currency and other details. These are then analysed by the software to identify patterns and behaviours that are inconsistent. Certain firms like Sanction Scanner also offer additional features such as powerful case management, full audit trails, user-friendly dashboard, live transaction screen and integrated sanction and PEP query. The company’s software also learns from the behaviours and patterns it catches, this helps you by improving accuracy over time. Let’s detail some of these features.
Key Functions of Transaction Monitoring Software
Real-time monitoring is pretty self-explanatory. It instantly tracks transactions to identify high-risk activity. However, rules engine may benefit from an explanation. Since there are numerous variables for both entities and firms, a certain degree of customization comes very handy. With rules engine, you can apply customizable scenarios and thresholds for detecting potential money laundering patterns. Then, there is alert generation. Again, it is self-explanatory. It flags unusual behavior and prioritizes alerts depending on the rules you have set. Case Management also deserves a mention, which allows your compliance teams to investigate, document and resolve alerts. The two last features of AML Transaction Monitoring Software we will mention are SAR/STR Filing and audit logs. It is not enough to detect and take action on suspicious activities, you also need to report these. These software can help you both report, and keep the necessary logs for audits and reviews.
The Tech Behind AML Transaction Monitoring
The technology used in AML transaction monitoring is brought together to each serve a different need your company might have. The first component is rule-based systems. These systems use international regulations to create rules. These rules are then used to flag suspicious activities. With tools like Sanction Scanner, you can create your own rules for flagging that best suit your company. Similar to this, behavioural analytics and anomaly detection are used to create patterns for each customer and then check their transactions by using said patterns to detect any anomaly among them. Machine learning and AI have been affecting every sector, and this process also benefits from them. Having an AI based system means your monitoring can be automated and updated according to new regulations. Machine learning helps since algorithms learn from every flag raised for suspicious activities and update their models accordingly. API integration is what makes it easy when you want to integrate transaction monitoring solutions into your own system, helping you have the compliance coverage your company needs.
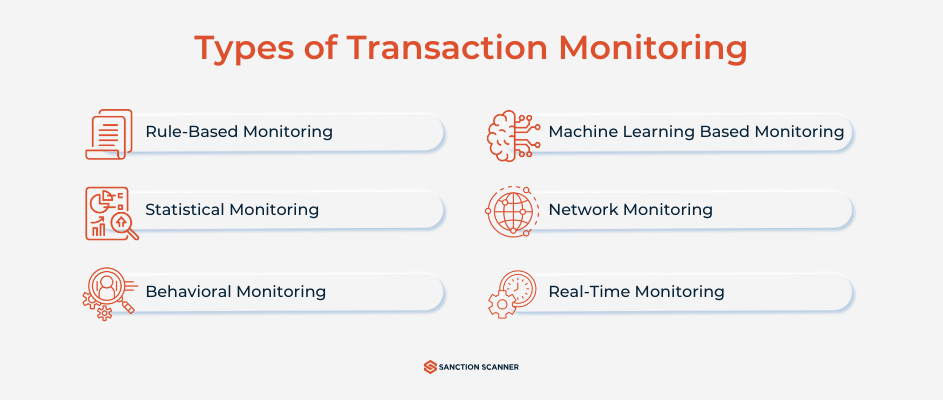
Types of Transaction Monitoring Systems
There are several types of Transaction Monitoring Systems. One of the most common methods is Rule-Based. It is very easy to understand and implement into your systems, however there is a high chance that you may encounter high false positives and its adaptation capability remains relatively limited to constantly evolving technologies. Having too many rules is another problem faced when operating with a rule-based method. While trying to cover all grounds when it comes to risks, your company may double its efforts trying to deal with every type of scenario. This is especially a good fit for banks and MSBs.
Next, there is a behavior-based system which can be ideal for Fintechs. It is particularly based on individual customer profiles to detect unusual behavior. However, it comes with its disadvantages such as its need for strong historical data and dependency on the data quality. There is also a more recent one that we should not ignore: Machine Learning Systems. These systems can learn and understand the behaviour of your customers and detecting suspicious activities accordingly. These are capable of identifying previously unknown or complex threats but this makes them more difficult to audit and explain. Thus, there can be challenges of regulatory transparency despite its efficiency. However, its effectiveness makes it a good contender for crypto businesses and VASPs. If nothing sounds particularly appealing, you may take a hybrid approach, which can combine rule-based and ML approaches. However, it is more complex to implement and maintain, which requires specialized expertise in your compliance team. This is particularly viable for scaling firms.
What Are the Red Flags in AML Transaction Monitoring?
Let’s talk more about what transaction monitoring focuses on. The first red flag we’ll mention is signs of structuring or smurfing. This is when large amounts of money is divided into smaller transactions to stay under the reporting thresholds. Another sign is rapid transfers being done to high-risk or entirely offshore jurisdictions. One other red flag we’ll mention is activity that is not consistent with the customer’s profile. This is why transaction monitoring uses behavioural analytics, the data is then used to detect inconsistencies. Once a dorman account suddenly starts making frequent transactions, it is another sign for the transaction monitoring process to detect and act accordingly.
What Is the Difference Between Transaction Monitoring and Screening?
We can summarize the differences between transaction monitoring and transaction screening two by underlining that; monitoring looks for suspicious patterns while screening identifies high-risk individuals. So, while the first one is concerned about behavior, the latter examines the individuals. Also, monitoring is an ongoing process, unlike screening. Lastly, their tools differ as well. Monitoring often uses rules and behavior analytics, while screening uses fuzzy matching and watchlists.
The Differences:
| Feature | Transaction Monitoring | Screening |
| Purpose | Detects suspicious behavior | High-risk individuals/entities |
| Timing | Ongoing, post-onboarding | Point-in-time |
| Scope | Transactions | Names vs. watchlists |
| Tools Used | Rule engines | Fuzzy matching |
| Outcome | Alert + case + STR/SAR | KYC decision |
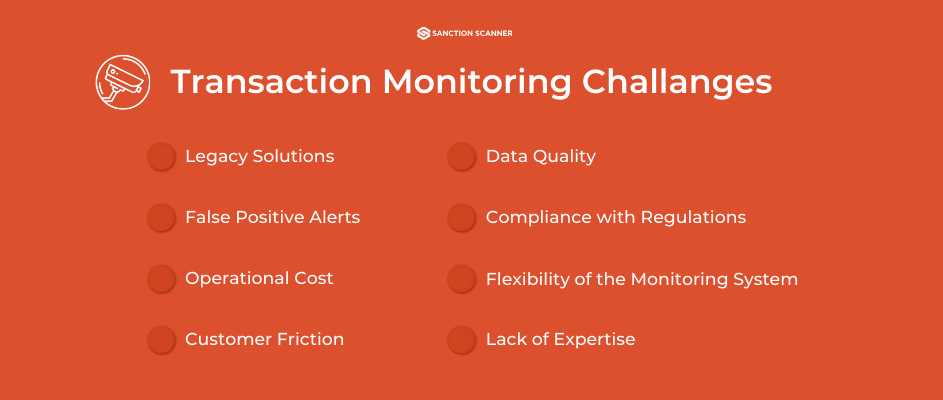
What Are the Challenges of AML Transaction Monitoring?
Compliance teams face many challenges when it comes to AML Transaction Monitoring, but high false positives could be the most common one. These both cause your compliance teams to get overwhelmed and increase operational costs. We have mentioned the types of monitoring systems in the previous paragraphs, as well as their disadvantages. However, traditional monitoring systems often fail to keep up with the constantly evolving methods of money laundering. This is mainly due to their reliance on static rules and thresholds. These rules lead to under-monitoring in some areas while over-monitoring in others. Also, preferring a conservative approach often comes with risks such as not being able to detect subtle or unusual suspicious patterns. This is exactly why we strongly recommend implementing artificial intelligence and machine learning. In our annual report, it is possible to see that the efforts on improving efficiency with automation and machine learning are on the rise. We can link the tendency of businesses towards these solutions to the analyst shortages and scalability demands of large transaction volumes. Which brings us to our last point: Analyst Resource Shortages. The demand for skillful AML analysts is very high and compliance teams often remain understaffed and under-resourced. All of this causes backlogs, delayed investigations and regulatory risk.
How to Set Up a Risk-Based Approach in Transaction Monitoring?
1. Segment Risks
The first step consists of identifying and categorizing the risks. There are three key metrics when it comes to segmenting the risks. You can classify customers as PEPs, high-net worth individuals or new-to-bank customers. Then, segment the product/service risk, such as trade finance, prepaid cards or crypto services. Lastly, categorize the geography risk. An entity may be sanctioned or come from high-risk jurisdictions. Our team at Sanction Scanner helps you create individualised scorecards for your customers. These are selected according to your company’s preferences and risk appetites, and will help you in the process of assigning a score to each customer.
2. Set Risk Tiers
In this part, there are risk tiers based on the exposure, such as low, medium or high, that you must assign customers and transactions. You should pay as much attention as possible on this part because doing so can save you both considerable time and resources.
3. Match Rules
After you set up the risks, there are a few actions that you must take accordingly such as tailor rules, thresholds and scenarios. For example, you may decide to apply a lower threshold for high-risk customer or enhanced monitoring for international transfers.
4. Sync Scores
This part consists of integrating monitoring with Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC) scores. If you do this properly, your business can achieve a very dynamic foundation that will allow you to rapidly see changes in customer behavior or risk exposure.
5. Document Everything
At this point, it shouldn’t be surprising that documentation comes as the last step. So, let’s detail what these documents should include: methodology, thresholds, decisions etc. During audits, you must have a clear rationale for the actions you have taken.
Penalties for non-compliance
Since transaction monitoring is an important part of AML compliance, not implementing the process into your systems may cause trouble for your company. Financial fines are the first penalty you may face for non-compliance. Firms get the largest fines when their AML framework and their risk profile don’t match. Your company should be using a compliance solution that is good enough and capable of supporting your company’s needs. Firms should be implementing effective monitoring systems, adhering to CDD obligations, and carefully checking against politically exposed persons (PEPs) and high-risk entities overall to avoid penalties. Monetary fines is the least your company can get. Regulatory restrictions, license suspensions, and reputational damage can be given as examples for severe consequences. Since these penalties are severe enough that they can end your company’s operations, we advise our readers to implement strong AML frameworks with modern transaction monitoring capabilities to avoid the consequences.
In July 2024, Deutsche Bank was fined $186 million for failing to fix ongoing transaction monitoring deficiencies despite multiple regulatory warnings. The regulatory fines an get bigger if your non-compliance is causing more severe problems.
How Sanction Scanner Supports Transaction Monitoring
Here at Sanction Scanner, we offer powerful case management, full audit trails, user-friendly dashboard, live transaction screen, integrated sanction and PEP query, and more. More than 800+ firms are using our tool to reach compliance. You can start to monitor transactions with ready-to-use rules. Sanction Scanner’s tool uses sources like sanctions lists, PEP lists, and adverse media lists. The sender and receiver’s names are checked against these sanctions lists every time to make sure there are no matches and the transaction can be completed. Sanction Scanner’s software also uses natural language processing (NLP) to analyse adverse media and then use any relevant information that could be about your customers. Moreover, you can set rules and create scenarios, which can reduce false positives by up to 96.99% and your workload by up to 80%. Also, we offer peer group analysis and advanced sandbox test environment, which allows you to test your rules.
Also, we offer peer group analysis and advanced sandbox test environment, which allows you to test your rules in different situations and choose the most optimized rule set. The sandbox feature will help you eliminate possible risks and give more time to investigate complex suspicious activities. Our interface requires no coding, you can just start using our features with drag-and-drop gestures.
You can also make your data fields that are specific to your company applicable to risk appetites by using dynamic fields. This product also offers dashboards where you can visualise all the data you’ve collected and the results you’ve gotten. There are different widgets like alert count by transaction type, closed transactions, customer risk level, open cases time distribution, open case time by user, and top 5 high volume customers will help you analyse your data better. The accounts trade can be analysed using the Transaction Analysis feature. Next, you can add your own blacklist and whitelist to your tool and customise accordingly. Your entire team can also use the system, there is no limit for internal users. Start by assigning different users to different tasks and see how efficient managing cases is using our tool.
Next, our RESTful APIs make sure the transaction monitoring tool is integrated into your product and ready to use within hours. Sanction Scanner’s API is powered by Webhook, and this way, we provide a two-way data transfer between Sanction Scanner and your project. This enables you to get help from the real-time alerts this transfer brings. Compliance teams can take immediate action thanks to this feature.
You can also use batch and manual methods whenever they are needed as alternatives. The batch is useful if you need to scan a large volume of transactions. Batch processing works by you uploading a list of transactions and sender-receiver details in an Excel file, the software does the rest by scanning. With the manual method, on the other hand, you can access the software using a web service at any given time and place. It allows you to use customized and ad-hoc monitoring. If you’re a smaller company with little resource, this option may be more favourable for you.
Sanction Scanner’s developer portal helps you by providing comprehensive documentation, sample code, Swagger docs, postman collection and SDKs. Developers can integrate our API and AML solutions using these resources. The portal also allows developers to use our sandbox environment for integration testing, and provides you with information about our webhook functionaly and how it can be integrated.
These are just a few examples of what we offer at Sanction Scanner. To learn more, do not hesitate to contact us.

FAQ's Blog Post
Transaction monitoring is the practice of analyzing customer transactions to identify suspicious patterns. It helps financial institutions comply with AML regulations and detect potential money laundering or fraud.
Transaction monitoring in AML refers to the process of tracking and analyzing financial transactions to detect suspicious activity that may indicate money laundering or financial crime.
Common types include rule-based monitoring, AI-powered systems, behavior analytics, and risk-based monitoring tailored to customer profiles and transaction patterns.
It works by applying pre-defined rules or machine learning algorithms to financial data to flag unusual transactions, generate alerts, and support investigations.
Steps include: Data collection Rule application Alert generation Case review Filing a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR/STR)
It helps financial institutions detect and prevent money laundering, meet regulatory requirements, reduce risk exposure, and avoid heavy fines.
Red flags include large cash deposits, unusual foreign transfers, rapid movement of funds, and activity inconsistent with customer profiles.
While not always mandatory, real-time monitoring greatly improves the ability to detect suspicious activity promptly and is considered a best practice.