What Are Government Regulations?
In this blog post, we’ll be talking about and explaining what government regulations are, the types of government regulations, and rules for business compliance. Government regulations are put in place by authorities to maintain order and protect people in the process. Some types of government regulations are economic, social, and administrative regulations. We’ll be talking about them more later. Since non-compliance can get your company fines and may ruin your reputation, complying with business compliance rules is important. There are several regulatory bodies that set forth regulations for companies to follow, while also checking whether they are complying with their regulations. One such regulatory body is the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) that aims to fight against money laundering and terrorist financing.
Another regulatory body that helps is U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC); SEC puts financial market rules that aim to protect investors against scams. In the EU, the regulatory body we’ll mention is the EU Commission; it aids companies by setting new rules and regulations that apply in the EU. Finally, the U.S. Congress is our last example for regulatory bodies that help with government regulations. This regulatory body passes laws that give more regulations; it, therefore, works to make sure your company safe.
Why Are Regulations Required?
These regulations are put in place so that companies and individuals are working in a transparent way that show responsibility and fairness. If there were no rules for compliance, crimes would explode and financial markets could become unstable as a result of going unchecked. The government acting as the ultimate control mechanism ensures both companies and customers are operating in a safe environment. You can also decrease your chances of getting fined and more if you are in compliance with these government regulations.
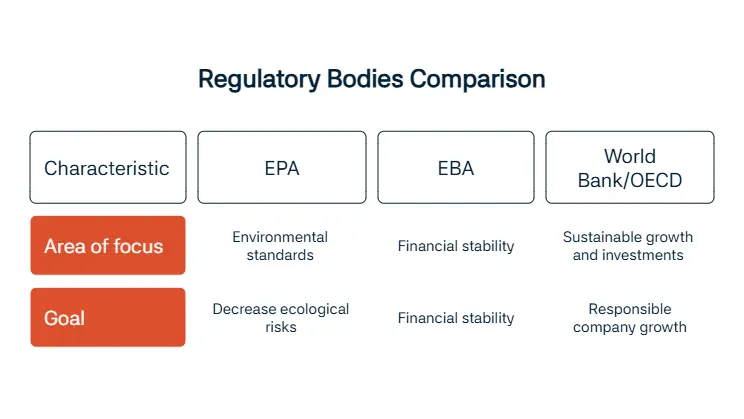
There are several regulatory bodies that perform regular controls to make sure you are in compliance with different regulatory bodies’ rules. There are different regulatory bodies for different categories. One example is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA); this regulatory body is there for making sure you are complying with environmental standards set forth that aim to decrease ecological risks. Another example is the European Banking Authority (EBA) which deals with financial issues and puts out guidelines that specifically helps with financial stability.
One other example we can give is the World Bank and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) which do similar work by regulating companies to ensure there are no shady business going on and that companies are growing sustainably, and encouraging invesments that are done responsibly.
How Do Federal, State, and Local Regulations Differ?
Federal rules apply worldwide and the rules set forth by them are more consistent, the US.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) can be given as an example since it enforces antitrust laws. Federal law gives a baseline and states then can impose more specific rules accordingly. The California Department of Consumer Affairs can be given as an example; they tailor federal level regulations according to their regional needs, compliance is managed by jurisdiction.
For the local level, these business laws are only working in their own district, interacting closely with businesses and real estate. Health codes, permits, and laws of similar nature are controlled by the local level regulations.
What Types of Government Regulations Affect Businesses?
In this part, we’ll talk about different areas of government regulations that are there for businesses to comply with. The first type is labor laws, these help with ensuring employees are treated fairly and working in an environment that is safe. In the U.S., the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) deals with figuring these standards out and protecting workers.
One other area is tax regulation meant for companies, financial reporting and transparency is ensured with these regulations. The implementation of blockchains requires monitoring and regulation of transactions, which is facilitated by the government authorities. Basel Committee is, for example, tasked with reducing risks in banking.
Governments also use regulation to achieve social, environmental and cultural objectives. So, another type is environmental business rules, which help businesses comply with requirements about emissions, waste disposal, and sustainable practices to make sure we have a safe future with decreased ecological risk. Specific regulations for different sectors are also handled by different regulatory bodies. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) deals with the medicine safety in the EU. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is another example we can give in a different sector; it is tasked with working about data privacy regulations.
How Do Regulations Influence Start-Up and Operating Costs?
Regulations must be thought of by our readers during every detail of process while starting a business. It is costly to reach regulatory compliance, making sure you are reaching tax requirements and reporting responsibly. Regulatory bodies like IRS will ask you to file your taxes, while FinCEN deals with anti-money laundering requirements. These examples show that there are different regulatory bodies that regulate different parts of a company.
You will also have to think of business licensing fees. These fees are needed to operate legally and they are different in every jurisdiction. Another thing our readers should consider to help them adhere to regulations is a compliance software. SaaS compliance platforms like Sanction Scanner and LogicGate, and are great options for helping you implement ongoing monitoring, reporting, and audit solutions. These software options are great for decreasing manual work and costs.
How Can Compliance Requirements Shape Business Strategy?
These requirements, of course, change how you move about when operating your company. The first way these requirements shape your business strategy is a compliance driven strategy; lots of companies use and recommend this strategy since it helps you comply with regulations set forth by regulatory bodies. Open Banking UK regulations have changed many companies’ outlook on their operations; complying with Open Banking UK’s regulations improved these companies’ services.
Another impact is the regulatory impact on product design. Since in sectors like pharmaceuticals and tech safety, privacy and testing standards are really important in the final product, regulations make sure that these areas are covered and quality products are served.
ESG regulation influence also has become an essential part of business strategies thanks to compliance requirements. The European Green Deal and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CRSD) encourage firms with their regulatory requirements to embed sustainability to their business models. These requirements help reduce carbon emissions, disposals, and ensure that social interests are protected.
Why Do Some Regulations Foster Innovation and Market Growth?
Some regulations are great for pushing companies to offer new solutions and experiment in a safe way. One example we can give is regulations driving innovation in the financial sector. PDS2 and open banking regulations in the EU requires banks to secure their data, this helps fintech startups by helping them create innovative payment methods and other services.
One other example is about regulators like the US SEC Innovation Hub and the UK FCA Sandbox. These regulatory bodies regulate in a way that gives companies space to test their products and new business models in an environment where they are supervised about regulations. This helps companies avoid fines. Another way regulations bring market growth is by encouraging companies to implement RegTech for compliance. These companies need to invest in compliance softwares and such to help them avoid fines and operate in a way that is in compliance with regulatory bodies’ requirements.
How Do Environmental Regulations Affect Supply Chains?
Like we’ve mentioned above, environmental regulations affect companies since it gives them requirements they need to adhere to reach sustainability and protect ethics in the process. But how do they affect supply chains? We’ll talk about them now.
The first way these regulations affect supply chains is by making sure carbon compliance is reached. Companies should always try to monitor and reduces greenhouse gas emissions, including tracking scope 3 emissions; these cover emissions that are not direct, like coming from suppliers and product use. Regulations like EU Green Deal and Carbpn Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) helps encourage companies to track, reduce and report these emissions. Another way these companies are encouraged is the EPA rules that are implemented in the U.S. and the UN Global Compact. These frameworks helps companies by pushing them towards an approach that includes greener practices while operating. These regulations help you reach your company’s ESG goals with ease.
How Do Labor and Employment Laws Impact HR Policies?
Labor and employment laws shape HR policies since these laws are put in place to protect the workers of the company. Labors compliance rules that are set by the U.S. Department of Labor makes sure workplaces are safe, and they meet wage and working hour requirements.
On the other hand, pay equity laws ensure that workers get fair compensation regardless of their gender and other demographics that otherwise might affect their pay. Regulations like California Assembly Bill 5 (AB5) determine employee classification; worker positions are then decided according to these regulations, whether they are considered employees or independent contractors. This difference affects benefits, taxes, and protections. HR teams are responsible with adhering to these requirements within different company processes. Guidance from places like the Economic Policy Institute (EPI) is really helpful since they show you the way during your compliance journey.
What Is the Economic Impact of Tax and Fiscal Regulations?
We’ll now talk more about how tax and fiscal regulations impact your company and its economic activities. Firstly, corporate tax rules and fiscal regulation impact leads companies’ decisions when it comes to choosing resources, pricing products, and planning expansions. To stop tax avoidance, the OECD BEPS 2.0 framework and the global minimum tax are put in place. These initiatives ensure fair taxes around the world. IRS in the U.S. and HMRC in the UK encourages rules of the same nature. G20 Finance Ministers are also working to achieve and maintain tax fairness worldwide.
How Do Data-Privacy Regulations Affect Digital Transformation?
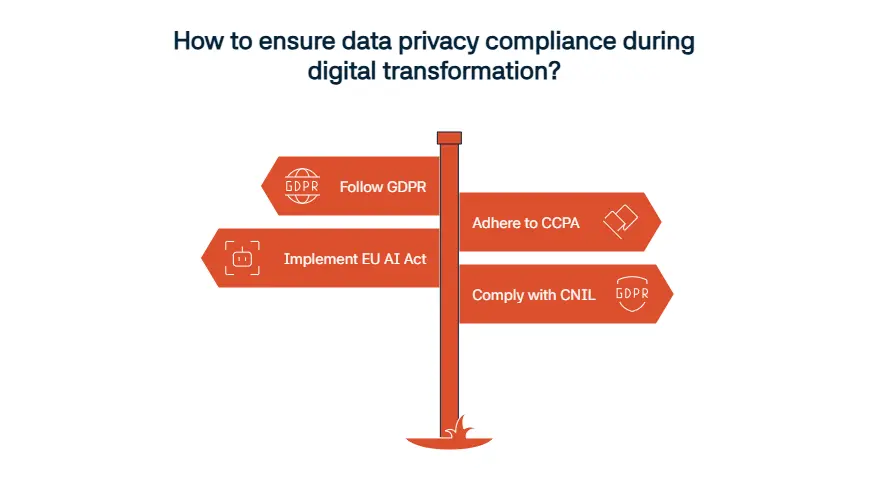
Since data privacy regulations are there to help you figure out how to collect and store information, they have a big role in digital transformation. Data privacy compliance is really important and we advise our readers to follow laws like GDPR, CCPA, and the EU AI Act to ensure they are implementing secure systems that are helping with transparency. These laws also led with user consent. Another thing to keep in mind is the cross-border data rules. These rules are different in every jurisdiction and companies should act accordingly. For example, if you are operating in France, you should know to comply with CNIL regulations.
When Should Businesses Review and Update Internal Compliance Controls?
Businesses should review and update internal compliance controls regularly since these are really important for your company’s well-being. After major regulatory updates, companies should act accordingly and follow soon after. Some examples are SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act), ISO 37301, or AMLD6, or during big changes like when internal processes or business operations are updated.
Internal audit compliance reviews are also essential to help you figure out if there are some gaps in your records. Another thing that is needed is having a set compliance review frequency, this is done to make sure you are always checking your company for AML compliance. For example, on May 12, 2025, the U.S. Department of Justice announced a major overhaul of its corporate enforcement policy. These major changes implemented by government bodies show that your company needs to be ready for continuous monitoring and updates when needed.
How Do Regulatory Impacts Differ Across Regions?
Different regions implement regulations that are similar but there are, of course, some differences as well. In the U.S., the U.S. Corporate Transparency Act is known for focusing on corporate ownership disclosure. On the other hand, the EU CRSD is well-known for its sustainability reporting and helping reach ESG goals in the EU. In Latin America, LGPD that’s operating in Brazil helps with data privacy. In Asia, regulatory bodies like MAS that operate in Singapore puts forth strict compliance regulations.
Which Sectors Are Most Sensitive to Rapid Regulatory Shifts?
We’ll be talking about the sectors that are the most sensitive when it comes to rapid regulatory shifts. The first sector on our list is fintech. These companies are subject to constant change and this is most likely caused by the increase of digital use and ever-changing AML and CTF techniques used by fraudsters. Regulatory bodies like FATF, FCA, and OFAC deal with ensuring compliance in this sector.
Another sector affected is the manufactoring sector; this sector is affected by ESG regulations like the CBAM that requires companies to reduce emissions and complete sustainability reporting. The healthcare sector is another example we can give. Regulatory bodies like the FDA makes sure these companies operate in a way that ensures safety, privacy, and consistency.
How Can Small and Mid-Sized Enterprises Adapt Cost-Effectively?
If you’ve read our blog post closely, you should realise that your company can benefit greatly from adapting to meet compliance requirements. But how so? Compliance tools for small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) and RegTech for small business can help a lot. Some examples are Sanction Scanner and SumSub; these companies help you by offering ongoing monitoring, reporting, and risk management to save you time and resources.
Shared services for AML and other regulatory obligations that are put forth by regulatory bodies like FinCEN help SMEs when reaching their standards. Another thing we can advise signing up to programs like SME Grants under EU Horizon, which helps provide financial support for SMEs that are looking to invest in compliance software and training.
FAQ's Blog Post
Government regulations affect small businesses by raising compliance costs but also building trust through consumer protections.
Government regulations mainly cover environmental laws, labor laws, tax policies, consumer protection, and industry standards.
Government regulations benefit businesses by creating fair competition, improving product standards, and increasing public trust.
Regulatory changes affect business planning by creating uncertainty, forcing quick adaptation, and often raising compliance costs.
Businesses that fail to comply with regulations risk fines, legal penalties, shutdowns, and reputational damage.
Environmental regulations impact manufacturing by requiring cleaner technologies and waste management, which raise costs but encourage sustainability.
Governments regulate online businesses through data privacy, digital taxation, cybersecurity, and consumer protection laws.
Businesses stay compliant by tracking regulatory updates, training staff, and using compliance software for ongoing monitoring.




