The United Kingdom has a notable global financial influence (£10 trillion in financial transactions conducted annually) and extensive banking infrastructure which puts it into an exemplary place for money laundering activities. The need for enacting robust Anti-Money Laundering laws and practices to combat money stems from the importance of preserving the integrity of its economic system and maintaining its international reputation as a reliable financial hub.
What Is the UK’s Approach to Anti Money Laundering?
The UK has several rigorous and collaborative approaches to anti-money laundering (AML) since it is always situated in middle of the danger of money laundering due to its intense financial activity.
The Importance of AML in the UK
In today’s world, money laundering may allow illicit activities like drug trafficking, corruption, and terrorism, but at the same time, it also poses a significant risk of disrupting economic stability and endangering national security. The economic impact can be directly felt through illicit funds infiltrating the financial system which can distort markets, destabilize industries or harm legitimate businesses. Furthermore, UK needs to maintain its position as a leading financial center which is basically built on the trust. This trust can be secured by upholding AML standards. This way, there will not be any damage done to its global reputation. Last but not least, it may also concern the national security in that money laundering can be used to support organized crime and terrorism.
Balancing Risk in the UK’s Financial System
As we have pointed out in the previous paragraphs, the UK has a remarkable financial activity. This is especially due to London’s dominance in global foreign exchange and its role in facilitating a vast volume of international transactions. Expectedly, there is an ongoing increase in exposure to the financial crime, thus robust AML frameworks are indispensable if a business wishes to mitigate these risks without dealing any damage to the country’s financial prominence.
UK Regulations and FATF Membership
The international body that establishes AML standards is called the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the UK is a member of this organization. This membership allows the UK to work closely with international partners and thus, strengthening global AML systems and combating financial crime across borders.
What Are the Main AML Laws in the UK?
The UK has implemented a robust legislative architecture to combat money laundering. Below are the primary laws that serve as the foundation of the AML framework.
Proceeds of Crime Act 2002 (POCA)
Any act of converting, using, or possessing the proceeds of crime as well as introducing mechanisms for recovering criminal assets through confiscation and civil recovery is criminalized under POCA.
The Money Laundering Regulations 2017 (as amended)
It serves as a detailed AML compliance requirement guide for businesses that includes precise guidelines of customer due diligence (CDD), ongoing monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities. Also, the 2019 amendments helped further reinforcing the compliance mechanisms to align with the EU’s Fifth Money Laundering Directive (5MLD).
Terrorism Act 2000
With the Terrorism Act 2000, the UK aims to criminalize the financing of terrorism and mandate financial institutions to report transactions suspected of contributing to terrorist activities in alignment with AML objectives with counter-terrorism efforts.
Economic Crime Act 2022
Well, this is a more recent one and it was introduced to combat economic crimes such as money laundering. The Economic Crime Act 2022 requires UK-registered companies to declare their beneficial ownership in order to enhance transparency measures so that loopholes that criminals exploit to hide illicit funds can be closed.
Which Authorities Regulate AML in the UK?
The enforcement of the UK's AML laws involves several specialized authorities and each of them are responsible for overseeing compliance within their jurisdiction.
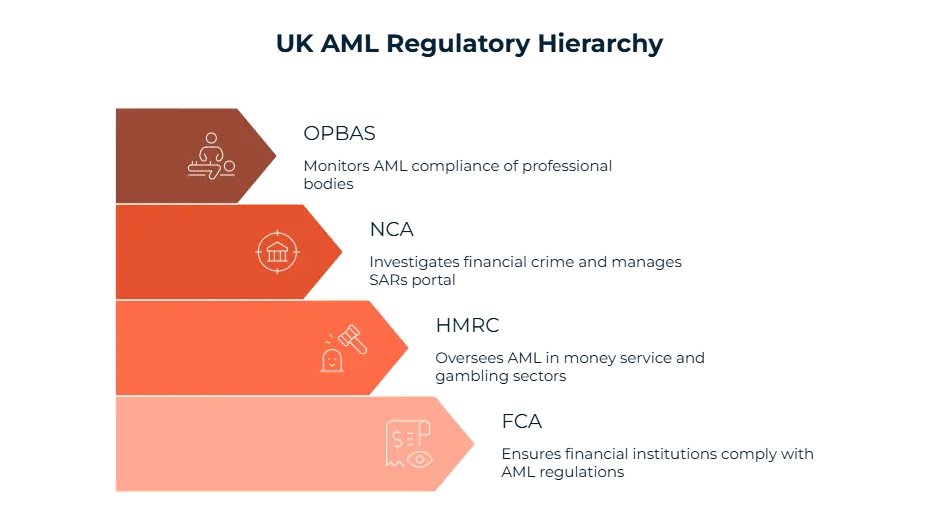
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) seeks to ensure that the financial institutions comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and in case of non-compliance, these banks, payment providers or other entities are held accountable.
HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC)
The role of HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) is much more specific, it oversees AML measures for industries such as money service businesses and gambling operators by checking whether these sectors have effective systems in place or not.
National Crime Agency (NCA)
The National Crime Agency (NCA) leads the fight against money laundering by investigating and prosecuting financial crime as well as maintaining a portal named Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) which provides businesses with a platform to report suspected instances of illicit activity.
Office for Professional Body AML Supervision (OPBAS)
The Office for Professional Body AML Supervision (OPBAS) monitors and guides professional bodies which can be exemplified by accountants and lawyers. Its goal is similarly ensuring the compliance of these organizations with AML requirements and enforcing supervisory practices.
What Are the AML Requirements for Businesses in the UK?
The amount of the AML requirements to adhere in alignment with national and international regulations for businesses operating in the UK is quite numerous.
Firstly, businesses must verify customer identities through CDD but it should be noted that for higher-risk customers, Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) may be required. Businesses must acknowledge that this is a continuous fight, so it is a must for businesses to regularly monitor customer transactions, in case any unusual pattern comes up. If any unusual or suspicious activity arises, AML requirements necessitate that it must be reported to the NCA via Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). Another thing to comply is to retain records of customer transactions and due diligence for at least five years, since they may be needed for future audits or investigations.
How Do AML Obligations Differ by Sector in the UK?
AML obligations in the UK differ based on industry, reflecting the unique risks each sector faces.
1. Banks and Financial Institutions
Banks and financial institutions are required to invest in sophisticated transaction monitoring systems, conduct enhanced customer due diligence (EDD), report suspicious activities through SARs due to their daily high value transaction handling.
2. Lawyers, Accountants, and Tax Advisors
The role that lawyers, accountants and tax advisors play in identifying money laundering risks is non-negotiable. They are responsible for verifying clients’ identities through KYC processes, assessing the legitimacy of funds involved in transactions and monitor for unusual activity and also reporting any suspicious activity to authorities via SARs, as we have seen in the previous section.
3. Real Estate Agents and High-Value Dealers
It is true that real estate transactions involve substantial amounts of money, so they should never be overlooked. Agents carry a big responsibility in this regard. They must scrutinize source of wealth to ensure legitimacy, implement KYC procedures and again, submit SARs in case they detect any suspicious behavior.
4. Cryptoasset Businesses and AML Licensing by FCA
This is a rather new domain but this doesn’t necessarily mean that it lacks any regulations compared to the first three categories. FCA has been mandating AML registration for crypto business in the UK since 2020 and it is a must for them to perform through due diligence on customers, monitor all crypto transactions, submit SARs and comply with all FCA rules.
Major Money Laundering Cases in the United Kingdom
| Year | Entity / Individuals | Fine / Outcome | Key Issues Identified | Enforcement Body |
| 2012 | HSBC | $1.9 billion global settlement | Lax AML controls, laundering linked to Mexican drug cartels | US DOJ / FCA |
| 2017 | NatWest | £264 million fine | Failure to monitor £365m in cash deposits by one client | FCA |
| 2021 | NCA v. Zamira Hajiyeva | £22m asset seizure | Unexplained Wealth linked to foreign PEP spending in Harrods | National Crime Agency |
| 2022 | UK Property Market | £117m frozen in UWO cases | Suspicious high-value property acquisitions by foreign nationals | NCA |
| 2023 | Barclays (Whistleblower) | Internal investigation | Allegations of delayed SAR reporting and ignored red flags | FCA / Internal Audit |
| 2024 | Crypto OTC Desk (London) | £8 million forfeiture | Unlicensed exchange, structuring, use of anonymizing tools | Metropolitan Police / FCA |
How Does the UK Apply a Risk-Based Approach to AML?
It is called risk-based approach when entities focus their resources on areas that pose the greatest risk of money laundering. However, there is not a “one-size-fits-all” compliance model so organizations must adapt measures based on the specific risks they face.
What Is a Risk-Based Approach in AML?
If we are to apply risk-based approach in AML, then firstly we had better assess the specific money laundering risks associated with their industry, geographic regions and customer base. Then, tailor internal controls and protocols proportionally to manage identified risks. And continuously monitor, update and improve measures as new risks emerge. It should again be underlined that businesses should allocate resources where risks demand the most attention instead of taking “a mile wide but an inch deep” approach.
UK’s National Risk Assessment (NRA)
The UK’s National Risk Assessment (NRA) is developed by the HM Treasury and the Home Office and provides a comprehensive evaluation of risks across sectors. The performed analysis are usually in the industries like banking, real estate, and emerging fields like cryptocurrency. To give a few examples, vulnerabilities associated with cash-intensive businesses examined by the NRA or the misuse of corporate structures such as shell companies.
FCA Expectations for Firm-Level Risk Assessments
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) enforces risk-based principles across financial services firms. It expects entities to conduct periodic firm-wide risk assessments in detail and assess risks posed by products, services, and delivery channels but also to evaluate customer risk and implement enhanced due diligence (EDD) measures respectively. If a firm doesn’t adhere to these requirements, they may face significant consequences ranging from repetitional damage to regulatory penalties.
Sectoral Guidance and Proportionality
The UK provides sector-specific guidelines to assist business like the one of Joint Money Laundering Steering Group (JMLSG), which offers tailored recommendations for financial institution or rather, sectoral guidance for real estate, accounting, and legal professionals operating within unique risk environments. Should it be necessary to address what the proportionality principle is, it is in fact a crucial RBA component that ensures measures are neither excessive nor inadequate to verify that a small firm is adopting measures adapted to its scale.
What Are the Penalties for AML Non-Compliance in the UK?
Non-compliance with AML regulations results in severe consequences in the UK. Financial and criminal penalties send a clear message about the importance of adherence.
Civil vs. Criminal Penalties: Civil penalties cover significant fines or disqualifications but when it comes to criminal penalties, the repercussions are much more heavier. They may result in legal prosecution, imprisonment, or in fact, a combination of both.
FCA Enforcement Examples: The FCA has demonstrated a firm stance on enforcement, there are two fine examples we can give in this regard: NatWest (£265 million fine in 2021 for failing to prevent money laundering risks.) and HSBC (£63.9 million in 2021 for AML monitoring system shortcomings.). These cases underscore the FCA’s zero-tolerance policy toward systemic vulnerabilities.
Directors’ Liability and Sanctions: Senior management carries personal accountability for AML failures. Directors and compliance officers may face individual penalties, including substantial fines and disqualification orders. This reinforces the expectation of a “tone at the top.”
What Are the Trends in AML Compliance in the UK?
Since it is driven by technological advancements and evolving regulations, AML compliance in the UK continues to go through changes with new regulations and requirements being introduced regularly day by day.
Economic Crime Plan 2 (2023–2026)
The UK’s Economic Crime Plan 2 lays out strategic objectives to combat money laundering and financial crime by strengthening public-private partnerships, improving transparency in ownership information and digitizing regulatory compliance.
FATF Evaluation Outcomes
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recently evaluated the UK’s AML regime and assigned high ratings for effective enforcement but there are still some areas to improve, which include the need for more robust risk assessments in emerging sectors like cryptocurrency.
Crypto AML Regulation Evolution
Cryptocurrency adoption and its associated risks increase in parallel. Fortunately, the UK has expanded regulatory measures for crypto exchanges by requiring detailed risk assessments, Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, and cross-border transaction monitoring.
AI and Technology in Compliance
Day by day, AI tools are reshaping AML efforts by leveraging algorithms for real-time transaction monitoring, advanced behavioral analysis and automated Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) filing to improve detection rates, reduce false positives, and optimize resource allocation.
What Are the Red Flags for Money Laundering in the UK?
Understanding common red flags are vital for businesses to proactively combat money laundering. By way of example, transaction structuring/smurfing, third-party payments or offshore accounts, abnormal customer behavior and using shell companies.
How Can We Help Your Business in UK?
Sanction Scanner empowers businesses to meet the UK’s rigorous AML standards with confidence.
· Real-Time Transaction Screening
Compare transactions against global sanction and PEP lists instantly.
· Suspicious Activity Monitoring
Simplify SAR processes thanks to our built-in compliance tools.
· Customized AML Modules
We also offer tailored solutions for high-risk sectors like crypto and real estate.
Sanction Scanner’s seamless integration with FCA and FATF requirements can ensure your business to have a comprehensive compliance strategy.
FAQ's Blog Post
The UK’s main AML laws include the Proceeds of Crime Act 2002, the Money Laundering Regulations 2017, and amendments from 5MLD. These establish requirements for customer due diligence, suspicious activity reporting, and risk assessments.
AML laws are enforced by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), HMRC, and the National Crime Agency (NCA), depending on the sector.
A SAR is a report submitted to the UK’s National Crime Agency when a firm suspects potential money laundering or terrorist financing activity.
Financial institutions, accountants, real estate firms, crypto asset providers, and other regulated sectors must comply with AML regulations under UK law.
Firms must assess the level of money laundering risk for each client and apply proportionate due diligence measures. High-risk clients require enhanced due diligence (EDD).
Firms should review AML policies regularly and upon changes in legislation, business model, or risk exposure.
The FCA supervises AML compliance for financial institutions, ensuring firms meet regulatory obligations and taking enforcement action when necessary.





