Money laundering is a significant concern that affects economies worldwide. It refers to the practice of disguising illicit funds through a series of intricate transactions, making it hard to trace the origin of the money. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance is a critical strategy used to detect and prevent money laundering. The process involves implementing policies and procedures aimed at identifying suspicious activities that may lead to money laundering. One of the techniques used in money laundering is layering, which we will examine in this article.
Money Laundering and AML Compliance
Money laundering is the process of concealing illicit funds obtained through criminal activities such as drug trafficking, fraud, and corruption. It can have a devastating impact on the economy as it undermines the integrity of financial systems and facilitates the growth of criminal enterprises. To address this issue, AML compliance is implemented to detect and prevent money laundering. AML compliance involves conducting risk assessments, customer due diligence, and transaction monitoring to identify and report suspicious activity. It is critical to the effective functioning of financial institutions and ensuring the stability of the economy.
Layering in Money Laundering
Layering is a technique used in money laundering that involves the creation of a complex web of transactions to conceal the origin of illicit funds. This process includes moving the funds through multiple accounts and transactions, often in different jurisdictions, to make it difficult to trace the source of the funds. The use of shell companies, offshore accounts, and complex financial instruments is also common to achieve this purpose.
Moreover, the main objective of layering is to distance the illicit funds from the criminal activity that generated them. By creating a veil of secrecy, the money launderer hopes to evade detection by financial institutions and law enforcement agencies. Furthermore, multiple transactions and accounts are used to create confusion and make it challenging to trace the funds back to their source. This makes it difficult to prosecute offenders, and the lack of transparency in the financial system facilitates the growth of criminal enterprises.
Layering is an essential component of the money laundering process and presents a significant challenge to AML compliance efforts. It is crucial for financial institutions and regulatory bodies to remain vigilant and take proactive measures to detect and prevent this illegal activity. The consequences of not addressing money laundering can be severe, as it undermines the integrity of financial systems and poses a threat to national security.
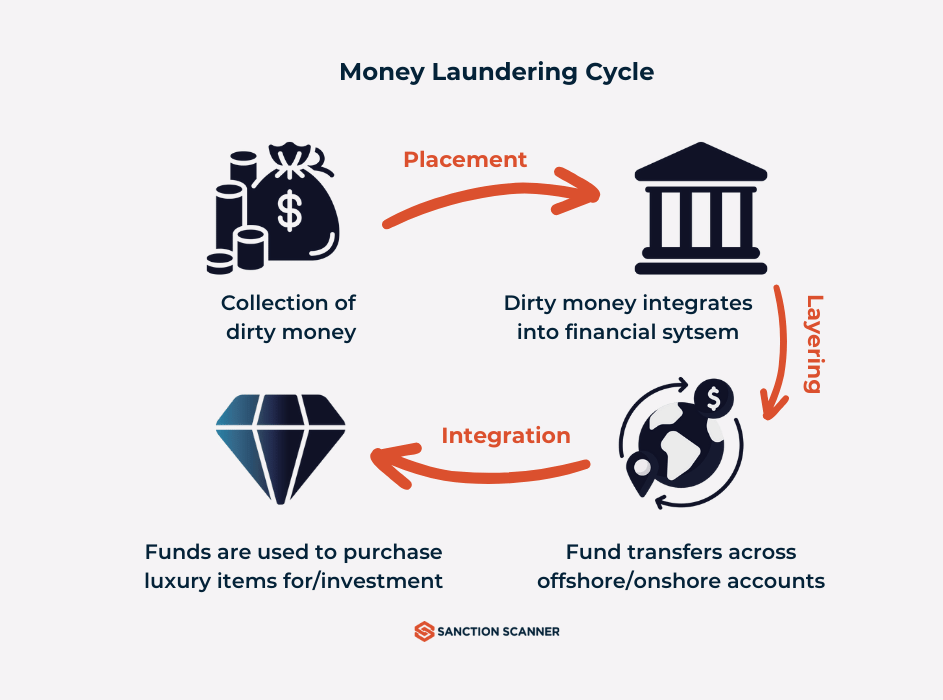
Stages of Money Laundering and the Role of Layering
Money laundering typically involves three stages: placement, layering, and integration. In the first stage, illicit funds are introduced into the financial system through various means, such as cash deposits, wire transfers, or the purchase of assets like real estate or luxury goods. This stage is crucial for the success of money laundering, as it allows criminals to move their ill-gotten gains into the legitimate financial system. Once the funds are in the financial system, they can be moved through a series of complex transactions using layering techniques.
In fact, layering is a technique used in the second stage of money laundering, where the illicit funds are made to pass through a series of complex transactions to create confusion and obfuscate the source of the funds. The aim is to create a veil of secrecy that makes it challenging for anyone to detect illegal activity. This technique involves moving the illicit funds through multiple accounts and transactions, often in different jurisdictions, using shell companies, offshore accounts, and complex financial instruments.
The purpose of layering, in the context of money laundering, is to create a distance between the funds and the original criminal activity, making it difficult for law enforcement to detect and prosecute offenders. Financial institutions play a crucial role in detecting and preventing layering by implementing AML measures that involve conducting risk assessments, customer due diligence, and transaction monitoring to identify and report unusual activities that may indicate money laundering. By identifying suspicious activities and reporting them to the relevant authorities, financial institutions help in preventing the integration stage, where the illicit funds are reintroduced into the economy as clean funds.
AML Compliance and the Detection of Layering
AML compliance plays a crucial role in identifying and preventing layering in money laundering. This is achieved by implementing a range of policies and procedures aimed at detecting suspicious activities. A key element of AML compliance is conducting risk assessments, customer due diligence, and transaction monitoring to identify and report any unusual activities that may indicate money laundering.
By complying with AML regulations, financial institutions can detect and prevent layering in money laundering activities. A key aspect of AML compliance is reporting any suspicious activity to relevant authorities. This enables law enforcement agencies to detect and prevent layering in money laundering activities by alerting them to potential criminal activities.
Furthermore, transaction monitoring is a crucial tool in AML compliance measures. It can help detect unusual patterns of behavior that may indicate layering activity. The analysis of transactional data can reveal complex patterns of activity that suggest money launderings, such as the use of shell companies, offshore accounts, and complex financial instruments.
The effective functioning of financial institutions is vital to ensuring the stability of the economy. AML compliance measures play a critical role in detecting and preventing layering in money laundering activities, which can have severe consequences for the financial sector and wider society. By adhering to AML regulations, financial institutions can help ensure the integrity of the financial system and prevent financial crime.
Conclusion
In fact, it is essential to note that AML compliance is not just about implementing policies and procedures to detect and prevent money laundering; it is also about maintaining a culture of compliance within the organization. This means ensuring that all employees understand the importance of AML compliance and are trained to identify and report suspicious activity. Failure to comply with AML regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and reputational damage.
All in all, money laundering is a significant threat to the integrity of financial systems around the world. Layering is one of the key techniques used by money launderers to conceal the origins of illicit funds. AML compliance plays a crucial role in detecting and preventing layering by implementing policies and procedures to identify and report suspicious activity. It is essential for financial institutions to prioritize AML compliance and maintain a culture of compliance within their organizations to combat this illegal practice effectively. By doing so, we can help ensure the integrity of financial systems and prevent the growth of criminal enterprises.