What is Adverse Media?
For this blog post, we’ll be talking about adverse media and we will hopefully be educating our readers more about this subject. Adverse media is information that is public and negative, it is about a person or company; these information are known for indicating potential criminal or unethical activity the person or the company is committing. Resources like news articles, court records, watchlists, blogs and forums, and social media platforms are common sources for adverse media screening.
What is Adverse Media Screening?
Adverse media screening helps companies immensely when figuring out whether a person or company is safe. It the the process of compiling negative news and making a decision about these new to determine how risky said person is. Obvious examples of adverse media include reports about individuals or organizations involved in money laundering, terrorist financing, corruption, or other financial improprieties.
Why Does Adverse Media Screening Matter in AML Compliance?
For this part, we will be talking about the importance of adverse media screening when reaching AML (anti-money laundering) compliance is your goal. Adverse media screening is important since it helps identify clients that pose a higher risk. It also assists in Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) processes that is required when dealing with high-risk customers. It also helps prevent crimes and ensures regulatory compliance. Meeting regulatory requirements recommended by FATF guidelines, EU AML Directives, and FinCEN is another benefit using adverse media screening brings.
Since adverse media screening helps with these steps, it will surely aid you in your quest to reach AML compliance.
What are the Regulatory Expectations from Adverse Media Screening?
Adverse media screening is more than a suggestion from us. It is also required under the guidance of regulatory bodies like FATF in the U.S. and AMLD in EU. Some other regulatory bodies that gives this guidance is FCA in the UK, and FinCEN.
How Often Should Adverse Media Screening Be Conducted?
Adverse media screening can either be done periodically or continuously. Conducting ongoing monitoring will help your company greatly. It will make sure you are not missing any detail in the meantime.
How Does Adverse Media Screening Work?
Let’s talk more in detail about adverse media screening. James Hannan, a risk specialist at Opoint says adverse media screening often slips under the radar due to the fact companies still treat it as an optional add-on rather than essential. We will be explaining how adverse media screening aids you and your company. Firstly, adverse media screening starts by setting search parameters. With these parameters it sets ahead of time, it starts a search of global and local sources. The next step this screening takes is filtering our false positives. After completing these important steps, it is time for evaluating the findings. From the findings, the customer or company’s risk score is determined and updated accordingly.
What is the Purpose of Adverse Media Screening?
You might be wondering why you should implement adverse media screening within your company.
Adverse media screening firstly prevents crime and helps ensure that your company is safe from being in contact with suspicious or risky individuals or companies. Adverse media screening also protects your reputation by making sure you are not involved with these risky entities. It will also help you meet AML and KYC compliance standards that are set by the FATF, the EU, and FinCEN. Finally, adverse media screenings help strengthen EDD by providing an analysis of background for customers who are deemed higher risk.
What is an Adverse Media Screening Tool?
Our next step will be explaining what exactly the adverse media screening tool is, since it might be difficult to imagine just by reading above. An adverse media screening tool is a software that helps automate negative news checks. This tool achieves this goal across multiple sources. By using this tool you will not only save a lot of time, you will also make sure your compliance standards are not compromised.
Manual vs. Automated Adverse Media Screening: Which One Fits Your Compliance Needs?
When comparing adverse media screening tools, you might think that a manuel system is better for your company. This is not correct, and we will now explain further to show you why. Manual adverse media screening is a slow process. Since you’re doing the research manually, things are bound to be slower and your results are therefore limited. Low volume of results might mean that there is a chance you are missing an important piece of news about the entity you’re researching.
Automated adverse media screening is done by tools that can speed up this process. The result you get will be done in a faster manner and it will feature more results than a manuel search can bring. These results will also be more accurate when compared to a manuel search.
The table below compares both approaches:
| Features | Manual Check | Automated Tool |
| Time-consuming | Yes | No |
| Real-time monitoring | No | Yes |
| Language support | Limited | Multi-language |
| Accuracy | Inconsistent | High on NLP |
| Cost-effective | Labor-heavy | Scalable and efficient |
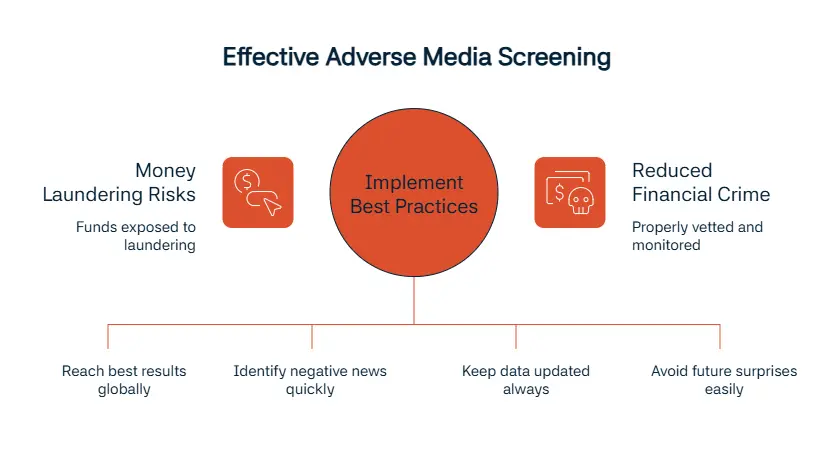
Best Practices for Adverse Media Screening
This part of our blog post will share more about the best practices for going forward with adverse media screening. Using both global and local sources will help you reach the best results while making sure you are missing no particular region.
The second item on our list is applying a risk-based approach (or RBA). Putting the customer or entity in a low, middle, or high risk cateogry will help identify the negative news quickly. Like we mentioned above, doing these screenings continuously will help immensely, and another critical point is keeping these data updated. After conducting your screening with the appropriate tool, documenting the outcomes you reach is important. Keeping your data and outcomes close to you by documenting them will make sure you will have no surprises in the future.
To give one example, Barclays Bank has been fined £42m by the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) for failing to properly vet or monitor clients Stunt & Co and WealthTek, exposing funds to money laundering risks. Stunt & Co was found suspicious and it was later uncovered that it was involved with a major laundering operation. And WealthTek, a simple FCA register check would have revealed, was not authorised to hold client money; its principal, John Dance, faces fraud and money laundering charges.
Are Adverse Media Screening and Negative Media Screening Different?
Our readers might be wondering whether adverse media screening and negative media screening are different things. These screenings are alike in nature and they are similar terms. One difference they have is adverse media screening being more compliance focused; the key difference is caused because of it.
What are Common Risk Indicators?
Now is the time to talk more about what we should be careful about when doing these screenings. How can we tell what is risky, and what is not? Our list below that is explained in detail will help you in your jorney of adverse media screening. The first thing to be careful about is criminal convictions or investigations. These are serious red flags that should not go unnoticed. The next big thing is links to sanctions or PEPs. You should watch our when seeing these.
Next up is fraud, bribery, corruption allegations. These allegations are serious and they play a big role in ruining a person or company’s reputation. Being involved with them will most likely harm your company as well. Another risk indicator you should look out for is tax evasion or insider training. These two are unforgivable financial crimes that definitely go against AML compliance. Human rights violations also indicate that odd activities are happening in the said company or with the said person.
Finally, coverage in credible news sources is our final risk indicator. This shows us that the negative news are front and center for those who are curious about the customer or company you’re involved with. Relying on unverified content such as social media posts or anonymous blogs can result in misleading assessments or name-matching errors.
What Are the Challenges in Adverse Media Screening?
Adverse media screening is a great tool for those who are looking to prevent themselves against people or companies who are risky to work with. But adverse media screening also comes with its challenges. One thing you can come across is false positives. These will negatively affect your research about the risky individual.
Having access to limited archives is another problem you might come across. This will make your research harder since you don’t have much to work with. Another challenge you might face when you are researching using adverse media screenings is the language barriers. These language barriers might halt your progress since you aren’t able to reach as much as you want. Finally, reaching these negative news is not enough by itself. You need to make sure the research you are conducting is getting help from credible sources. The lack of source credibility is another problem adverse media screening might face.
Examples of Valuable Regional Portals
We’ve mentioned above how important using global and local sources when conducting an adverse media screening is. Here are some examples from different regions of the world:
Firstly, El País and La Nación do great work in Latin America and because of it, they are popular and credible. Our second region is Asia. The Straits Times and Asahi Shimbun are great and well-known in Asia. The third region globally is Middle East. Al Jazeera and Arab News help immensely during adverse media screening since they are well-known. Finally, our last region is Africa. Daily Nation, Mail and Guardian are great sources for when conducting adverse media screening.
What Are the Key Adverse Media Screening Trends in 2025?
There are many trends for adverse media screening in 2025; in this blog post, we will be giving information about a few.
The first trend is AI-based context analysis. This is done to receive more accurate risk detection; AI helps get correct results quicker like it does in many other sectors. Another trend is local language NLP. Local language NLP helps get better regional coverage. Language barriers are eliminated by this way. Integration with ESG and reputational risk scoring is another trend we can see in 2025. This trend will make sure you are connecting with the right people or companies. One other trend we can give as an example is RegTech and SupTech collaboration. RegTech and Suptech collaboration helps with regulatory oversight.
Finally, real time continuous monitoring is on the rise. It is more favorable than periodic checks like we mentioned above before. These trends help reach greater results more efficiently.
How Does Sanction Scanner Simplify Adverse Media Screening?
We at Sanction Scanner help by conducting AI-powered searches that help you reach results faster. We also support 30+ languages which help with language barriers. We aid our customers by giving out real time alerts. Our software makes sure you receive low false positives, request demo now.
FAQ's Blog Post
It’s the process of searching for negative or unfavorable news about individuals or entities across trusted media and public sources.
It helps organizations detect early signs of reputational damage, financial crime, or regulatory risks before they escalate.
Credible news outlets, regulatory announcements, court records, and specialized industry databases.
Ideally on an ongoing basis, with continuous monitoring or scheduled periodic reviews.
Financial institutions, fintech companies, insurers, legal firms, and other regulated businesses.
Yes, it supports Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) by uncovering hidden risks.
Connections to fraud, corruption, money laundering, terrorism financing, or other criminal activities.