AML Solutions For Payment
We help to Payment in the AML compliance process with our next-generation AML solutions!

TRUSTED BY OVER 800+ CLIENTS
We bring solutions that will make it easier for our customers to comply with AML Regulations.








Protect your business with Real-time AML & PEP data updates
Sanction Lists, Pep Lists and Watch lists are updated every 15 minutes. Therefore, businesses must perform AML checks using updated data. Businesses can detect their customers in more than two hundred countries' real-time sanctions, PEP, and adverse media data using our AML screening.
+3000
DATA POINTS CHECKED
+220
COUNTRIES COVERED
15 min
ALWAYS REAL-TIME DATA
150 ms
SCANNING

Integrate As You Like
We provide API support for all our AML solutions. You can integrate your system with Sanction Scanner's Powerful APIs. You can use Name Search, Id Search, Passport no Search methods, create blacklists, whitelists via API. We won't save your data, but if you don't want to share your Customer Data with us, we have different & unique search methods for it.
“Sanction Scanner's software is easy to use, and we enjoy working with it. Since implementing its solution, we have significantly reduced false positives. The time and effort we previously spent on false positive alarms can now be directed towards other aspects of the business, which contributes to its growth.”

Guy Shaked
Legal Counsel at ironSource
“What I like best about Sanction Scanner is its real-time screening capability and automated alerts. It helps us detect potential matches instantly and take immediate action, which is critical for our AML compliance.”

Tolgahan Kapanci
Head of Compliance at PeP
“With Sanction Scanner, we offer a fast, easy, and secure customer onboarding process. Thanks to its enhanced scanning tool, we focus on real risks, not false positives. Thus, we can meet our AML obligations and our customers' expectations.”

Arda Akay
Chief Compliance Officer at Tom Bank
“Sanction Scanner provided us the most comprehensive database to screen our clients. It includes lists from all over the world and is always up-to-date.”

Gulnihal Akartepe
Global Vice President at TPAY
“With Sanction Scanner, we reduce the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing by controlling on local and international lists also to avoid risks during our onboarding process.”

Oğuzhan Akın
Experienced Banking & Expansion Manager (MEA) at WİSE
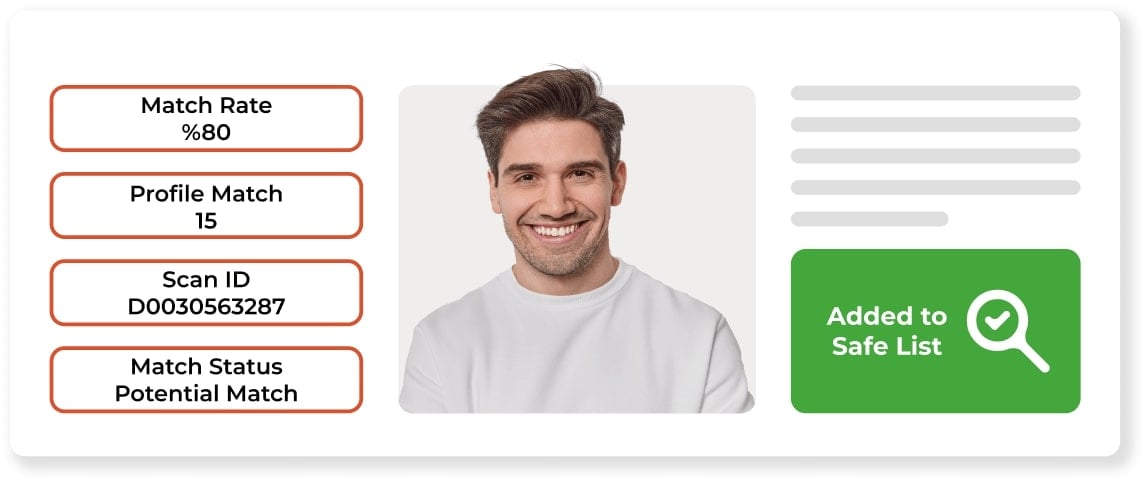








Transaction Screening Software for Payment Industry
Payment companies and money transfer companies have to control the transactions they mediate. The transaction Screening tool allows financial institutions to control the receiver and sender in our global AML data transactions. With API integration, all controls take place automatically in seconds in the background.



Transaction Monitoring Software for Payment Industry
Payment and Money Transfer companies can create their own rules and scenarios with AML Transaction Monitoring without any coding knowledge, so they can automatically detect high-risk and suspicious activities. Automate your transaction monitoring processes and reduce false positives with enhanced features.
Featured news and press releases
FAQs about Payment
Payment providers must conduct CDD, monitor transactions, report suspicious activity (SAR), and perform risk assessments to stay AML-compliant.
Payments are screened using AML tools that monitor transaction patterns, scan global watchlists, and flag anomalies in user behavior.
KYC verifies user identity using documents and biometrics, helping prevent fraud, fake accounts, and AML breaches from the start.
It detects laundering, fraud, and unusual behavior in real time—allowing teams to flag high-risk activity before it escalates.
Yes. Gateways must follow AML rules under frameworks like EU AMLD, FinCEN, and FATF—implementing KYC, monitoring, and reporting systems.
Red flags include structured transfers, sudden behavior shifts, multiple linked accounts, and inconsistent cross-border activity.
They use AI, fuzzy matching, and dynamic risk scoring tools like Sanction Scanner to prioritize true threats and reduce alert fatigue.
Yes. Crypto processors must perform KYC, monitor transactions, and report risks to align with global AML and VASP standards.
CDD verifies individual users, while MDD assesses merchants receiving payments—both essential to detect fraud and regulatory risk.
Look for solutions offering real-time screening, API integration, alert automation, and access to global PEP/sanctions lists—like Sanction Scanner.
Real-time AML screening checks users and transactions instantly against sanctions, PEPs, and adverse media before processing payments.
Yes. Recurring or subscription payments should be monitored to detect behavioral changes, usage of flagged cards, or jurisdictional risks.
Yes. Delayed or missed Suspicious Activity Reports can lead to regulatory penalties, especially in jurisdictions with strict timelines (e.g., 24–72 hours).
Geolocation data reveals if users access services from high-risk jurisdictions or use proxies/VPNs—helpful for detecting hidden risks.
P2P payments are vulnerable to laundering via account layering, anonymity, and fund fragmentation—making real-time monitoring essential.
Yes. These tools offer semi-anonymity, rapid fund movement, and are often used to bypass banking controls, posing higher AML risk.
KYB verifies the identity, ownership, and risk level of merchants or vendors using the platform key for B2B payment compliance.
By using layered identity checks like biometrics, document validation, and behavioral signals to spot artificially generated or stolen profiles.
Threshold alerts trigger when transactions exceed set limits, helping flag potential structuring, layering, or large illicit fund flows.
Yes. Scalable solutions like Sanction Scanner offer API-based AML tools that fit the budget and architecture of growing fintech startups.



