Singapore is a powerful player in the fight against financial crime. As a global financial hub, transparency and security are critical to its success. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) enforces Anti-Money Laundering regulations.
The potential impact of money laundering on assets, investor confidence, and criminal funding underlines the importance of strong AML measures. Singapore's framework requires stringent customer checks, transaction monitoring, and reporting. This culture of compliance strengthens responsibility in financial institutions.
Singapore's commitment extends globally, collaborating internationally. Going forward, it will refine regulations, embrace tech, and strengthen partnerships to maintain its leadership against financial crime.
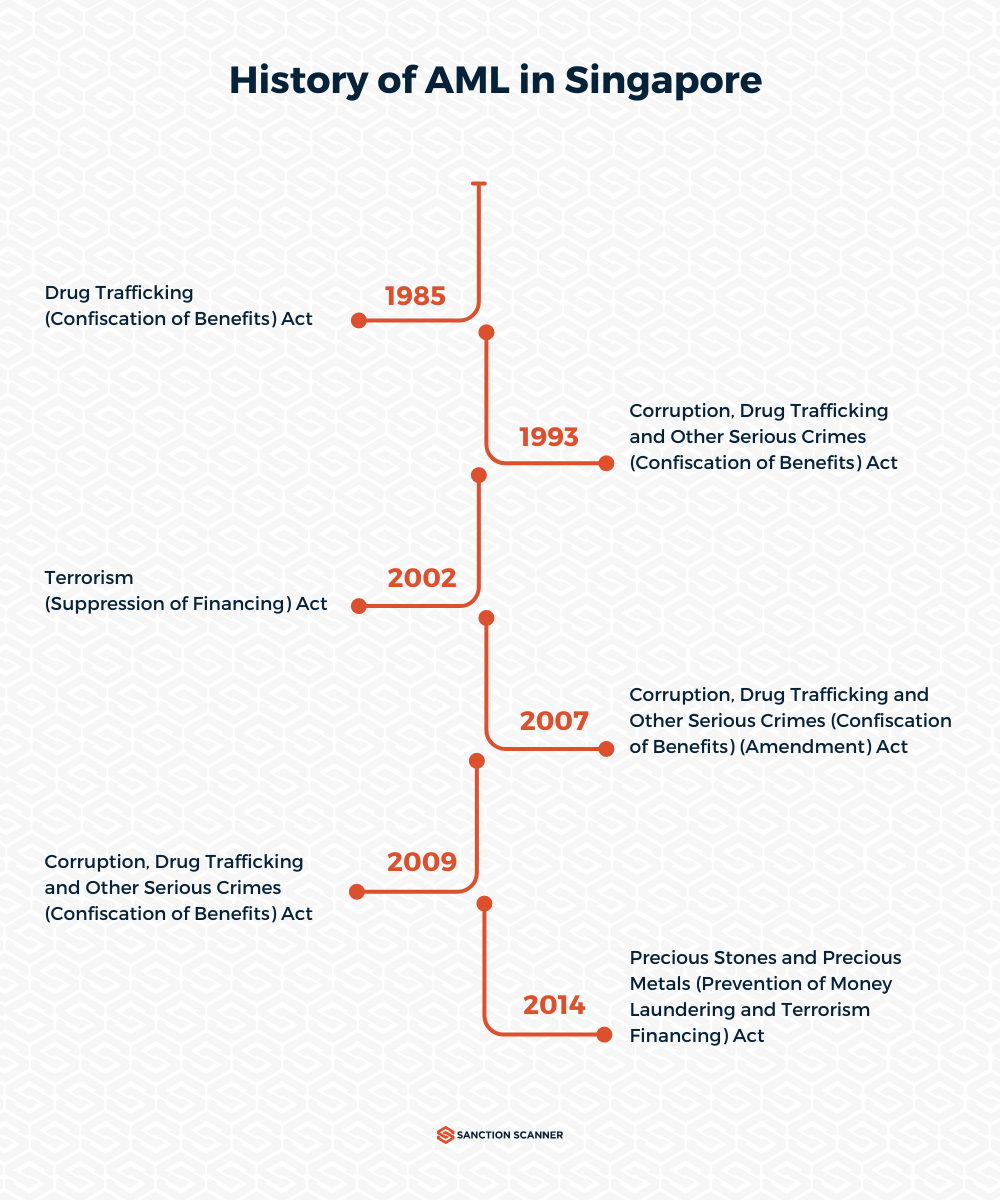
History and Legal Framework for AML in Singapore
Singapore's central bank, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), is instrumental in regulating financial institutions' AML compliance. It issues guidelines and conducts inspections to ensure adherence to robust AML standards.
Singapore's AML framework is reinforced by international cooperation through bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). The country collaborates with other jurisdictions in information sharing and extradition, demonstrating its commitment to tracking and disrupting cross-border illicit financial flows.
Key AML Laws in Singapore
- Corruption, Drug Trafficking, and Other Serious Crimes Act (CDSA): The cornerstone of Singapore's AML framework, the CDSA criminalizes money laundering and provides a legal basis for investigating, prosecuting, and confiscating assets from serious offenses. It empowers law enforcement and regulatory bodies to take action against suspected money laundering and supports asset forfeiture.
- Terrorism (Suppression of Financing) Act (TSOFA): Targeting terrorism financing, TSOFA makes providing funds to terrorist entities or individuals an offense. It mandates strict due diligence for financial institutions to prevent such financing, allowing authorities to freeze and seize associated assets while promoting international cooperation against terrorist financing networks.
- Precious Stones and Precious Metals Act (PSMTFA): Addressing money laundering risks in these sectors, PSMTFA extends AML and counter-terrorism measures to dealers in precious stones and metals. It enforces enhanced due diligence, licensing requirements, reporting of suspicious transactions, and compliance officer appointments.
- Securities and Futures Act (SFA): Regulating securities, futures, and financial advisory industries, SFA imposes AML obligations on licensed entities. It mandates customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting of suspicious transactions, ensuring vigilance in detecting and preventing money laundering and fraud.
- Computer Misuse and Cybersecurity Act (CMCA): Focusing on cybercrime, CMCA addresses computer-related offenses like cyber fraud and hacking. It enhances Singapore's capability to combat digital financial crimes and safeguard financial transactions in the cyber realm.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Although not solely AML-focused, PDPA governs personal data protection. Organizations are required to safeguard personal data, which indirectly contributes to fraud prevention by reducing identity theft and fraudulent activities.
These regulations are enforced by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), the central regulatory authority overseeing financial institutions' AML and fraud prevention compliance. MAS issues guidelines, conducts inspections and enforces action when needed to ensure adherence to these standards.
Government and Regulatory Role in AML
- Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): As the central bank and financial regulatory authority, MAS oversees AML efforts. It formulates policies, sets guidelines, and issues notice to financial institutions, instructing them on AML measures, due diligence, monitoring, and reporting. MAS conducts inspections, enforcing compliance through penalties, revocations, or prosecutions for deficiencies.
- Commercial Affairs Department (CAD): Part of the Singapore Police Force, CAD investigates and prosecutes money laundering. Collaborating with MAS and other law enforcement agencies, CAD identifies and disrupts money laundering activities. Specialized units gather evidence, initiate legal proceedings, and prosecute individuals involved in money laundering.
- Government Involvement: Singapore's government enacts comprehensive laws, such as the Corruption, Drug Trafficking, and Other Serious Crimes Act (CDSA) and Terrorism (Suppression of Financing) Act (TSOFA), criminalizing money laundering and terrorist financing. Legislation is regularly reviewed and amended to address evolving threats.
- International Cooperation: Singapore, a member of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), aligns its AML regime with global standards. The government engages in international initiatives to combat cross-border money laundering and terrorist financing and undergoes mutual evaluations to ensure compliance.
- Public-Private Partnerships: The government fosters collaborations between regulatory bodies, law enforcement, and the private sector. These partnerships facilitate information sharing, expertise enhancement, and joint efforts against financial crime. Such collaborations enable the implementation of effective AML controls and promote compliance within the financial sector.
Singapore's multi-faceted approach, involving regulatory bodies, government agencies, and international collaborations, ensures a robust AML framework that guards against financial crime.
Money Laundering Risks
Being a global financial and trade center, Singapore faces distinct money laundering risks due to its international connections and strong financial sector. While robust AML measures are in place, the country remains vigilant in addressing these risks:
- Trade-based Money Laundering (TBML): Singapore's significant role in trade creates a risk of criminals using trade transactions to launder illicit funds.
- Offshore Entities and Shell Companies: As a regional financial hub with an easy company setup, Singapore can be vulnerable to money laundering via offshore entities and shell companies, which hide ownership and complicate tracking illicit funds.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Singapore's well-connected financial system exposes it to cross-border money laundering. Correspondent banking and remittance services can be exploited for global fund movement, necessitating robust transaction monitoring.
- Real Estate Sector: The high-value real estate market is susceptible to money laundering, as criminals may seek to legitimize proceeds by investing in properties.
- Virtual Currencies and Fintech: Singapore's fintech prominence introduces risks related to money laundering through digital channels.
- Corruption and Bribery: Despite low corruption rates, there's a residual risk of laundering proceeds from corrupt activities.
Regulatory bodies like MAS and CAD continually assess these risks, collaborating with financial institutions to strengthen AML measures. They offer guidance, conduct inspections, and encourage information sharing to bolster Singapore's financial resilience against money laundering threats.
Overview of AML Compliance and Key Points in Singapore
Importance of AML Compliance: An effective Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance program is vital for both Singaporean companies and those associated with Singapore. Here's a summary of an AML program and key considerations:
- Risk-Based Approach: Companies must adopt a risk-based approach to tackle money laundering effectively. Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment helps identify specific money laundering risks. This ensures AML measures address the most relevant threats.
- Evaluate business activities: Understand industry vulnerabilities for tailored safeguards.
- Assess customer profiles: Identify high-risk individuals or PEPs for enhanced due diligence.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD):
- Transaction Monitoring for Fraud Detection: Singapore mandates robust transaction monitoring systems:
- Analyze transaction data: Detect deviations from patterns.
- Use risk models: Consider customer behavior and historical data.
- Utilize external data sources: Screen against watchlists and sanctions.
- Employ AI and machine learning for continuous learning.
- Reporting Obligations: Know Singapore's AML reporting requirements:
- Report suspicious transactions: Identify and report suspicions.
- Train employees: Enhance awareness of red flags.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Assess third parties' AML controls:
- Evaluate AML policies and procedures.
- Include AML obligations in contracts.
- Ongoing Regulatory Compliance:
- Stay informed: Monitor MAS updates and industry events.
- Analyze impact: Assess changes on existing AML frameworks.
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement.
Prioritizing AML compliance safeguards companies, preserves reputation, and bolsters Singapore's financial system integrity.
Revolutionize AML Compliance in Singapore with Sanction Scanner Solutions
Experience the future of AML compliance technology tailored for Singapore with Sanction Scanner. Our software is designed to adapt to Singapore's dynamic regulatory landscape seamlessly.
Sanction Scanner offers a comprehensive suite of tools to meet Singapore's diverse needs, ensuring you're prepared for evolving regulations and protecting your reputation. Contact us or request a demo to explore the future of compliance today!