Money laundering is often perceived as a shadowy, distant crime, but its repercussions are felt across the globe, infiltrating financial systems and economies in ways that are both profound and far-reaching. In 2020 alone, the UNODC estimated that the amount of money laundered globally in one year is 2-5% of global GDP, or $800 billion to $2 trillion. Understanding the role of international AML regulations is crucial to grasping the full scope of this issue. But what exactly is money laundering, and why should we be concerned about its far-reaching consequences?
What is Money Laundering?
Money laundering is the process of disguising the origins of illegally obtained money, typically by means of transfers involving foreign banks or legitimate businesses. The goal is to make the illicit funds appear legal, allowing criminals to enjoy their ill-gotten gains without attracting attention. This clandestine activity has evolved over the years, adapting to new technologies and regulatory measures, making it a persistent challenge for authorities worldwide.
How does Money Laundering work?
Money laundering involves three stages: Placement (introducing illicit funds into the financial system), Layering (obscuring the origins of the funds through complex transactions), and Integration (reintroducing the laundered money into the economy as legitimate funds). Understanding anti-money laundering processes can help identify these stages more effectively.
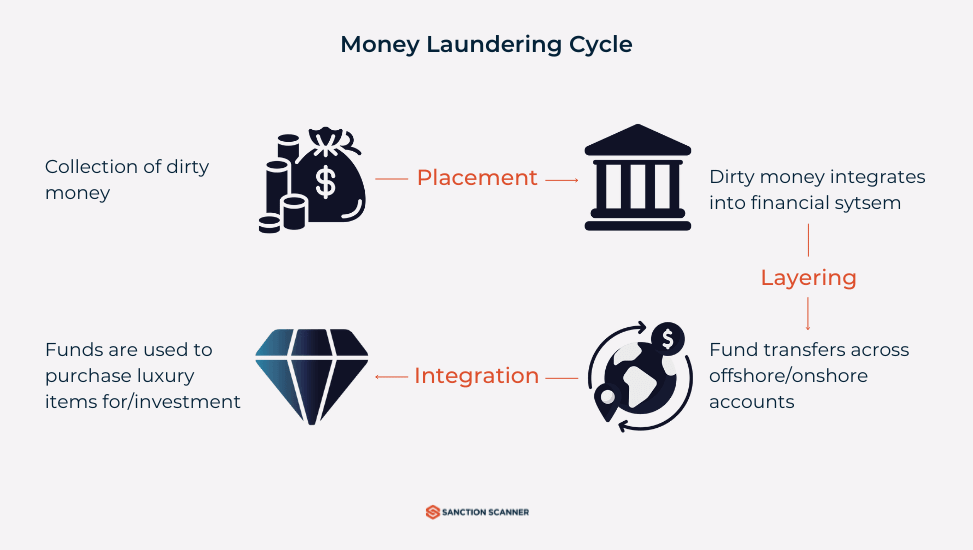
Why Money Laundering is a Global Concern?
The impact of money laundering extends far beyond the shadowy world of organized crime. It poses a serious threat to the global financial system, distorting markets, undermining economic stability, and eroding public trust in financial institutions. Governments lose billions in revenue due to tax evasion, which in turn affects public services and infrastructure. Moreover, money laundering is often linked to other forms of criminal activity, including drug trafficking, terrorism, and political corruption, further exacerbating its detrimental effects on society. The importance of AML compliance for businesses is essential to mitigating these risks.
Stay with us as we uncover the intricate web of money laundering and its profound implications for financial systems around the world.
The Economic Impact of Money Laundering
Money laundering is not just a legal issue; it has profound economic implications that can destabilize financial markets, distort currency values, and drain government resources. Understanding these impacts is crucial for grasping the full scope of the problem.
Distortion of Financial Markets
How Illicit Funds Affect Market Stability
Illicit funds, when funneled into legitimate financial systems, can create artificial demand for certain assets, leading to price inflation and market bubbles. For instance, the real estate market is a common target for money launderers. When large sums of illicit money are invested in property, it can drive up prices, making housing unaffordable for average citizens. This artificial inflation can lead to market instability, as seen in various global financial crises.
Impact on Currency Value and Exchange Rates
Money laundering can also distort currency values and exchange rates. When large amounts of illicit money are moved across borders, it can create significant fluctuations in currency demand. For example, if a substantial amount of laundered money is converted into a particular currency, it can artificially inflate its value. Conversely, sudden withdrawals of these funds can lead to sharp devaluations. Such volatility can deter foreign investment and disrupt international trade, further destabilizing economies.
Loss of Revenue for Governments
Tax Evasion and Its Consequences
One of the most direct economic impacts of money laundering is the loss of tax revenue. Money launderers often use complex schemes to hide their income, making it difficult for tax authorities to track and collect taxes. According to a report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), tax evasion linked to money laundering activities costs governments around the world an estimated $600 billion annually. This loss of revenue can have severe consequences for public finances.
Reduced Public Spending and Services
The loss of tax revenue due to money laundering and associated tax evasion means that governments have fewer resources to allocate to public services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This reduction in public spending can lead to a decline in the quality of life for citizens and exacerbate social inequalities. For example, in countries where money laundering is rampant, public hospitals may suffer from underfunding, leading to inadequate medical care for the population.
The Social and Political Consequences
Money laundering is not just an economic issue; it has profound social and political ramifications that can erode public trust, fuel corruption, and destabilize entire nations.
How Money Laundering Undermines Confidence in Financial Institutions
When financial institutions are implicated in money laundering activities, it severely undermines public confidence. Banks and other financial entities are expected to uphold the highest standards of integrity and transparency. However, when they are found to be complicit in laundering illicit funds, it shakes the very foundation of trust that these institutions are built upon. For example, high-profile scandals involving major banks have led to significant reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
The Ripple Effect on Society
The erosion of trust in financial institutions has a broader ripple effect on society. When people lose faith in the banking system, they may become less likely to save or invest, opting instead to hoard cash or engage in informal financial activities. This lack of trust can stifle economic growth and development, as financial institutions play a crucial role in facilitating investment and economic activity. Moreover, the perception that the financial system is corrupt can lead to social unrest and a general sense of disillusionment among the populace.
Links Between Money Laundering and Political Corruption
Money laundering and political corruption are often intertwined. Illicit funds are frequently used to bribe public officials, influence elections, and fund illegal activities. This creates a vicious cycle where corrupt politicians protect and enable money launderers, further entrenching corruption within the political system. According to Transparency International, countries with high levels of money laundering often score poorly on corruption perception indices, indicating a strong correlation between the two.
Case Studies of Countries Affected
Several countries have experienced significant political instability as a result of money laundering and corruption. For instance, in Brazil, the "Operation Car Wash" investigation uncovered a massive money laundering and corruption scheme involving state-owned oil company Petrobras and numerous high-ranking politicians. The scandal led to widespread protests, the impeachment of President Dilma Rousseff, and a prolonged period of political turmoil.
In another example, the Panama Papers leak exposed how politicians, business leaders, and criminals used offshore accounts to launder money and evade taxes. The revelations led to political crises in several countries, including the resignation of Iceland's Prime Minister and increased scrutiny of offshore financial centers.
Global Efforts to Combat Money Laundering
The fight against money laundering is a global endeavor involving a complex web of international regulations, standards, and technological advancements.
Overview of Key Organizations
Several international organizations play a pivotal role in setting standards and promoting cooperation to combat money laundering:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Established in 1989, the FATF is an intergovernmental body that sets international standards to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF's 40 Recommendations are widely recognized as the global benchmark for AML efforts.
- International Monetary Fund (IMF): The IMF provides technical assistance and policy advice to member countries to strengthen their financial systems and combat money laundering. The IMF also conducts assessments of countries' compliance with international AML standards.
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC): The UNODC works to assist member states in implementing AML measures and provides resources and training to enhance their capabilities.
Important Regulations and Their Impact
Several key regulations have been enacted to combat money laundering on a global scale:
- The USA PATRIOT Act: Enacted in response to the 9/11 attacks, this act significantly expanded the scope of AML regulations in the United States, including stricter KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements and enhanced due diligence for financial institutions.
- The European Union's Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD): The EU has implemented several AML directives, with the Sixth AML Directive (6AMLD) being the most recent. These directives aim to harmonize AML regulations across member states and enhance transparency in financial transactions.
Technological Advances in Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming the way financial institutions detect and prevent money laundering. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate suspicious activities. For example, machine learning algorithms can flag unusual transaction patterns that deviate from a customer's typical behavior, enabling quicker and more accurate detection of potential money laundering activities.
Future Trends in Anti-Money Laundering Technology
The future of AML technology looks promising, with several emerging trends poised to enhance detection and prevention efforts:
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain's transparent and immutable ledger can provide a secure and traceable record of transactions, making it more difficult for money launderers to hide illicit funds.
- RegTech Solutions: Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions are being developed to help financial institutions comply with AML regulations more efficiently. These solutions leverage AI, machine learning, and big data analytics to streamline compliance processes and reduce the risk of regulatory breaches.
See How Sanction Scanner Can Help
In the ever-evolving landscape of AML compliance, staying ahead of regulatory requirements and effectively detecting suspicious activities is crucial. This is where advanced tools like the Sanction Scanner come into play. Sanction Scanner is a comprehensive AML solution designed to help financial institutions, fintech companies, and other organizations navigate the complexities of AML compliance with ease and efficiency.
Sanction Scanner offers real-time screening of customers and transactions against global sanction lists, PEP lists, and adverse media. It utilizes AI and machine learning to detect money laundering activities and provides detailed reporting for compliance. Customizable solutions streamline the compliance process for your specific needs.
To see how Sanction Scanner can help your organization stay compliant and secure, request a demo today.


