Customer Risk Assessment
Strengthen your business with greater control compliance with risk-based scorecard review.

Preferred by 800+ businesses for detailed risk assessments.








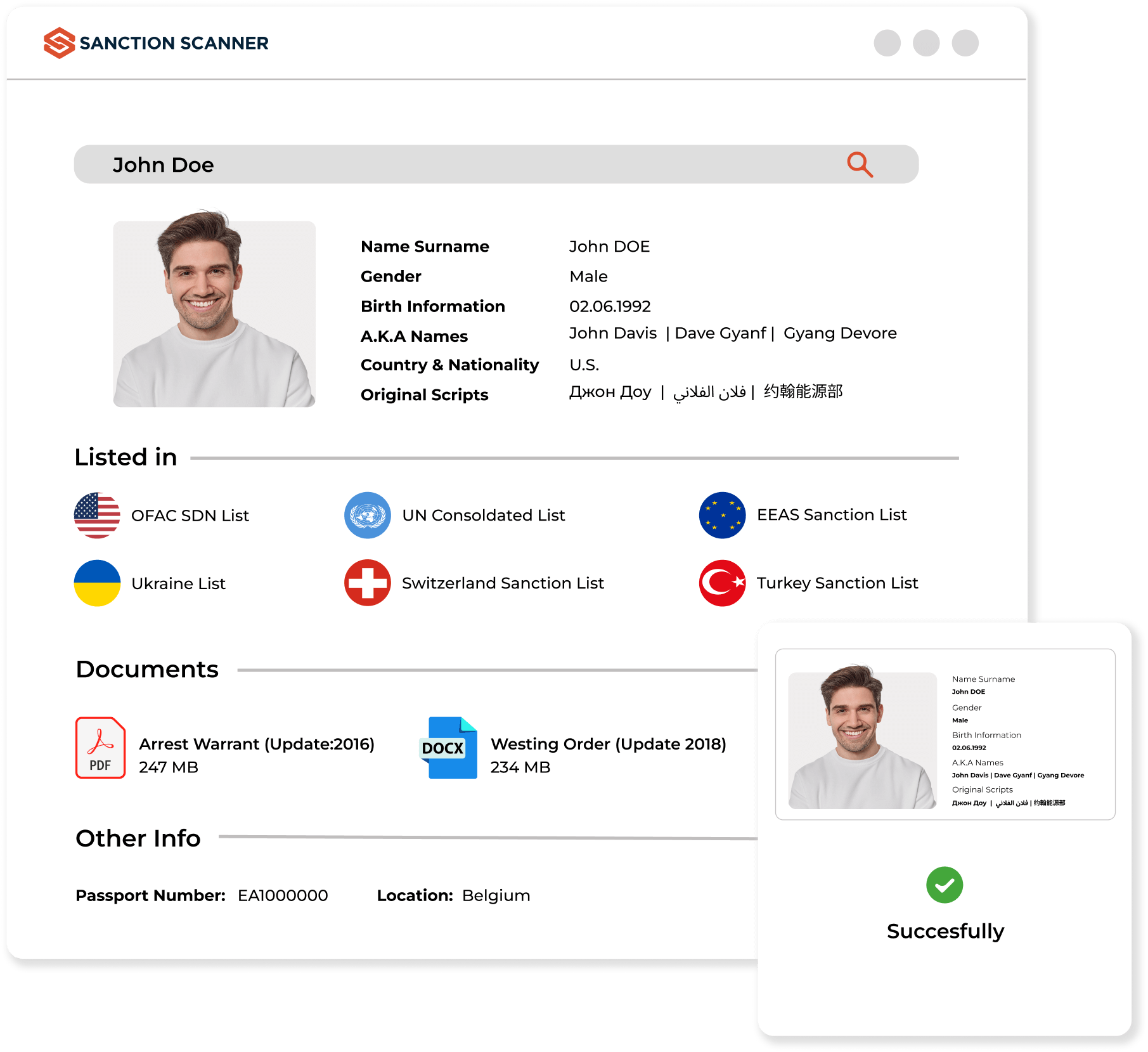
Risk-Based Scorecard
Institutions should conduct risk assessments to establish a level of risk for customers. Risk-based compliance management is used to visualize strategy and risk management data and inform decision-making. For example, you can strengthen your business with more control compliance, learn more about your risky customers, and use these risk assessment criteria in your rules with the risk-based scorecard review.
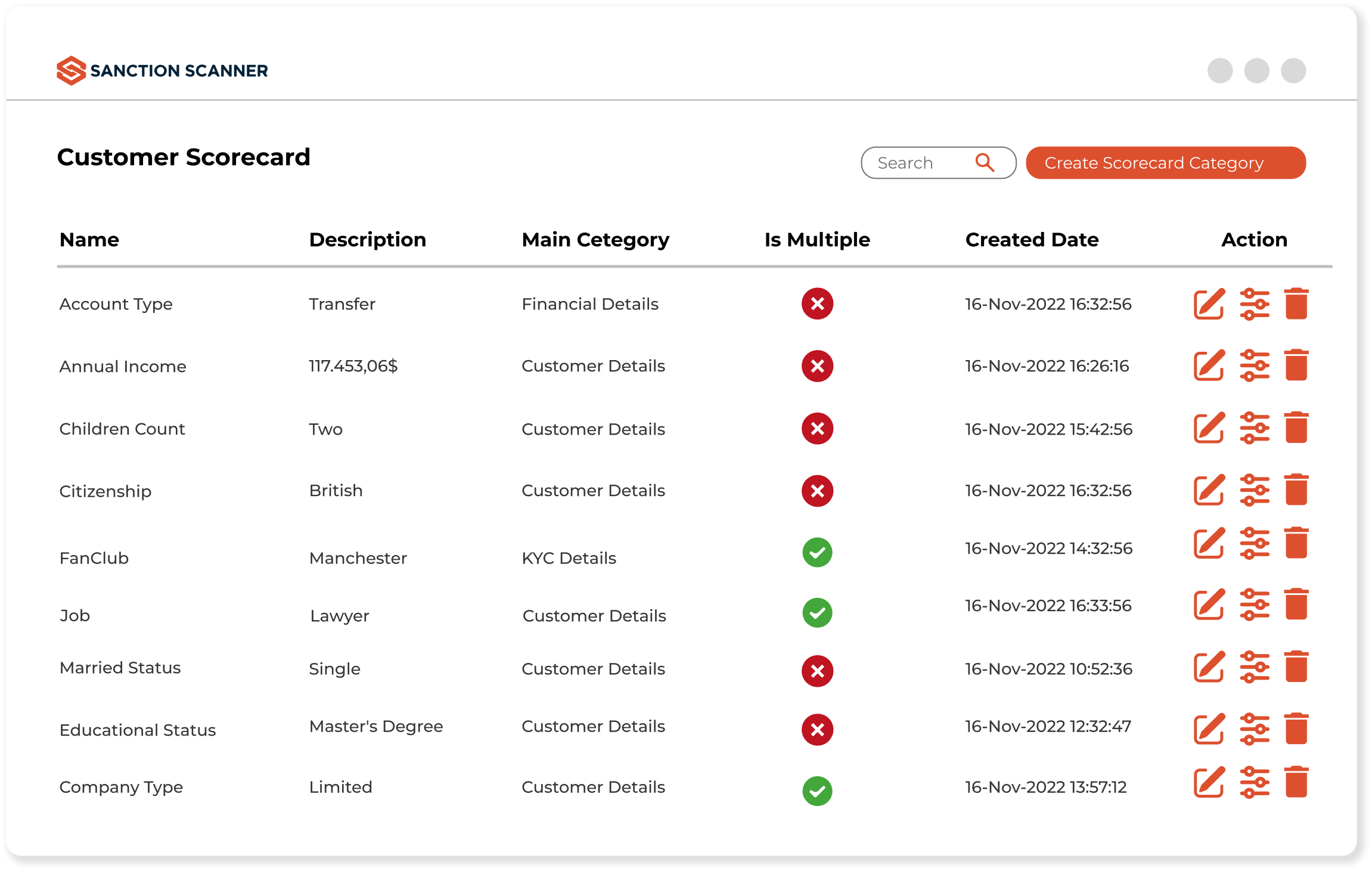
Write Rules to Build Your Own Risk Rating
With the dynamic rule writing feature, you can create the most appropriate rules and scenarios for customers' risk scores according to your risk appetite without writing code. Without writing your own rules, you can quickly integrate with Sanction Scanner's different ready-made rule sets suitable for every sector. You can fine-tune your rules and analyze customer risk.

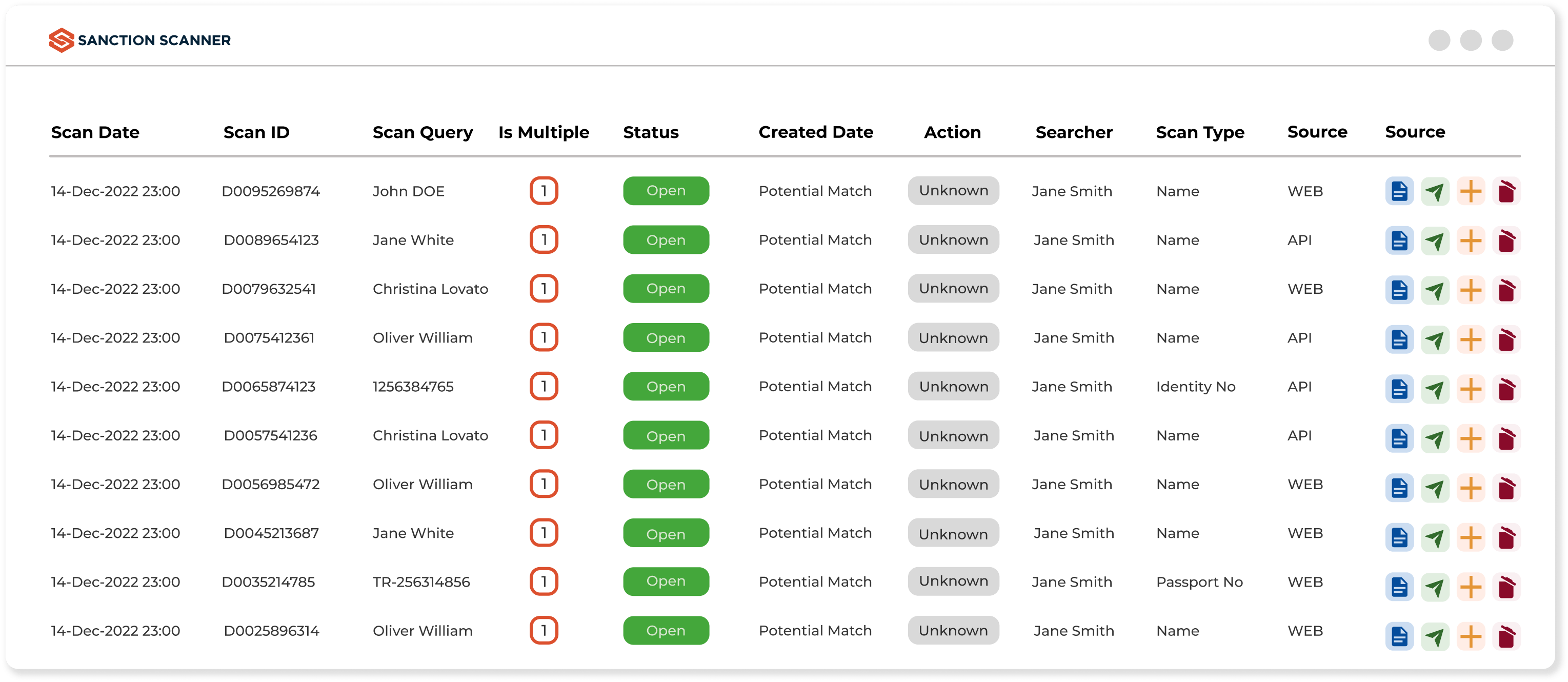
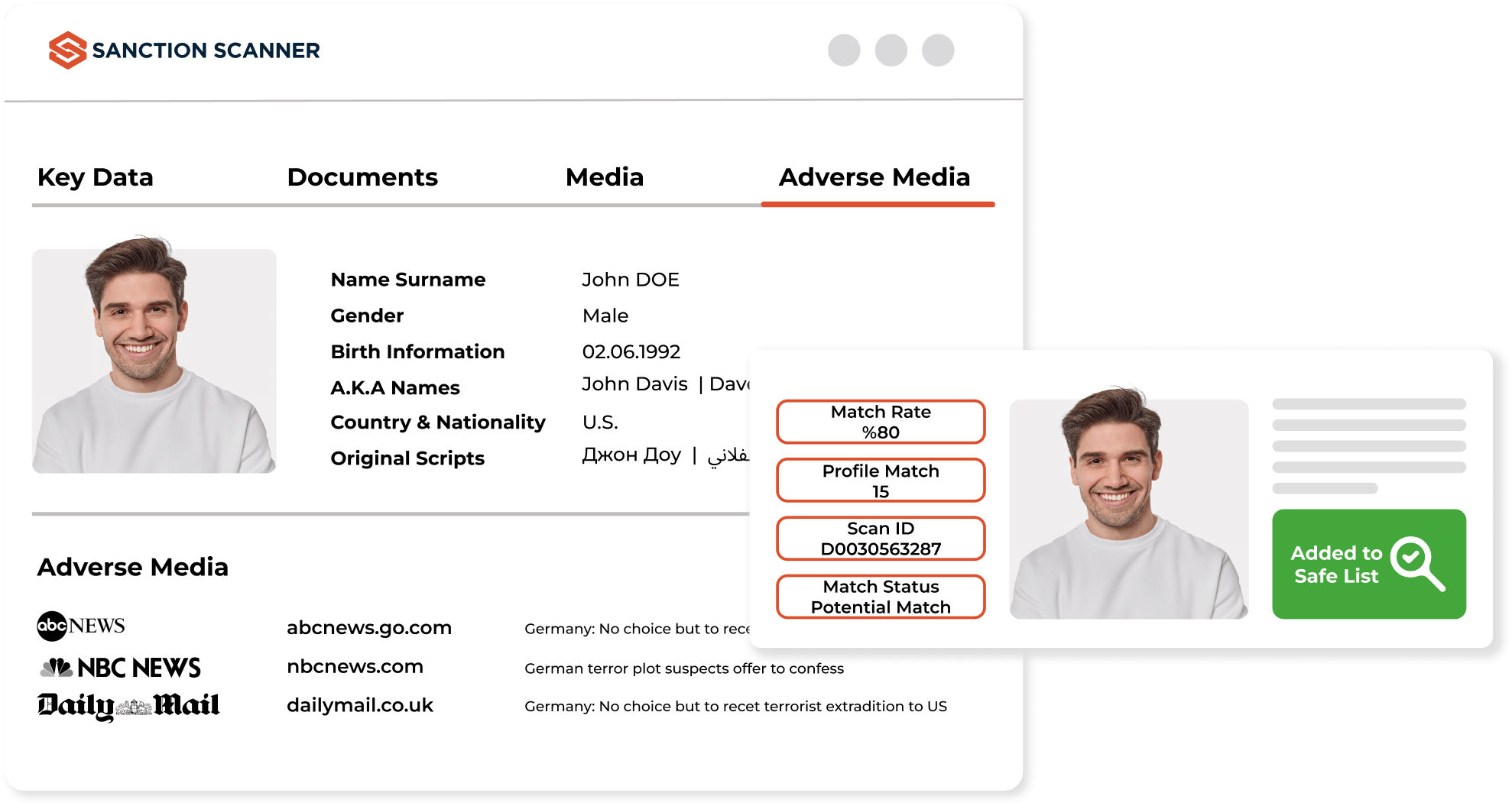
Customer Risk Analysis On Applying Scores & AI
You can assign risk points to your customers with the rules you have written according to your risk appetite. You can make an end-to-end risk analysis for your customer's thanks to the risk scores. Risk analysis is vital in any lending moment. According to risk analysis, you can make safe and fast decisions about your customers' activities and reduce your control workload.
Why is The Sanction Scanner Different?
Real-Time Data
Perform your Sanction and PEP control using real-time data.
Local List Management
You can add your local blacklist and whitelist to the system.
Parametric Monitoring Settings
Customize which lists you want to run your scans and match rate for your business.
Case Management
You can check your business' scanning history and access your old scans easily.
Enhanced Profile
View all results using one profile and determine the level of risk fast.
Reduce False Positive
Reduce false positives and strengthen your compliance process.
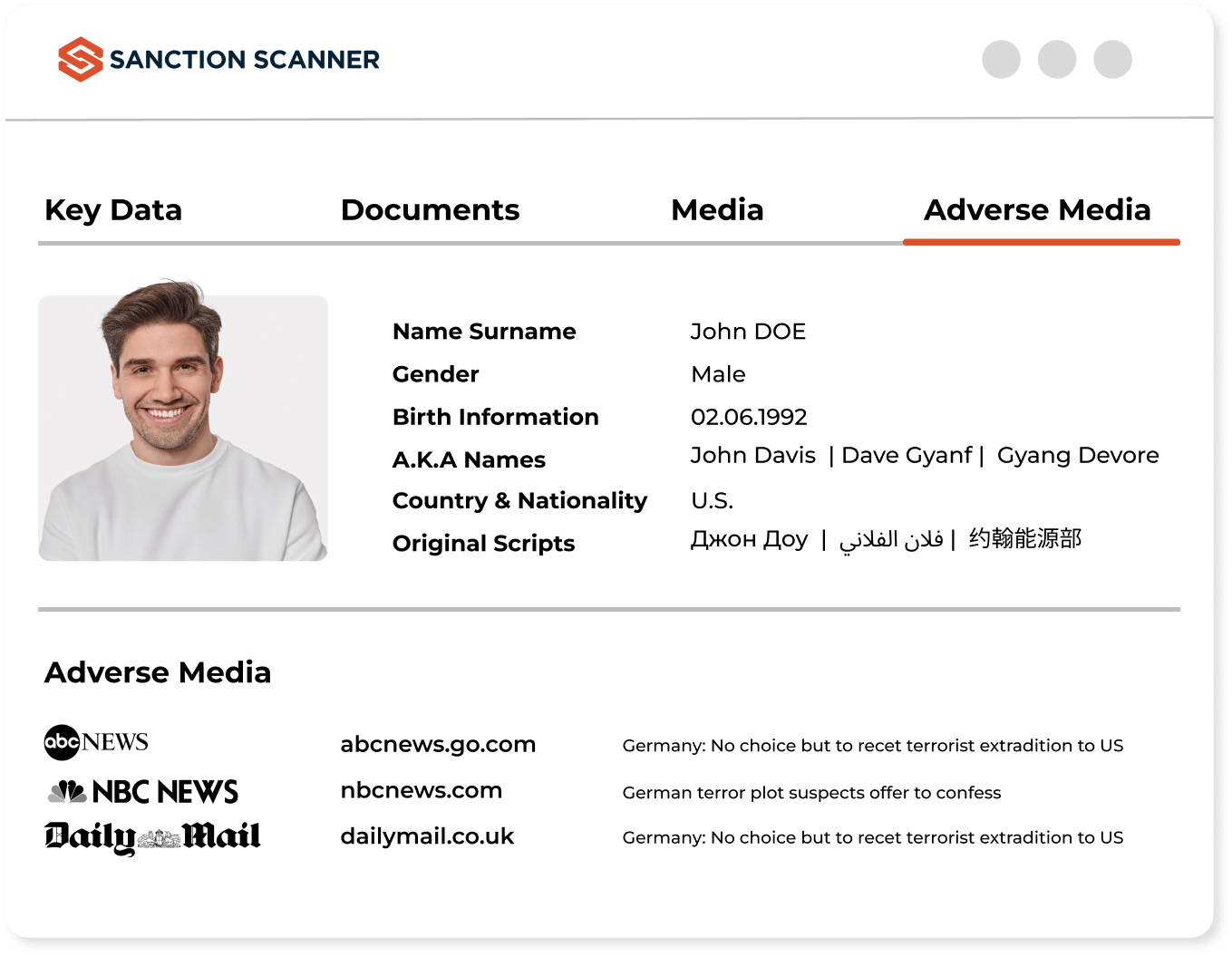
Set Customer Risk Levels
You can assign scores according to criteria such as your customers' profession, age, income, country, and currency, and you can easily make a risk assessment. According to these scores, you can define low, medium, high, and critical alarms. Then, you can easily decide on the action steps according to the alarms you receive during the transactions with your customers.
“Sanction Scanner's software is easy to use, and we enjoy working with it. Since implementing its solution, we have significantly reduced false positives. The time and effort we previously spent on false positive alarms can now be directed towards other aspects of the business, which contributes to its growth.”

Guy Shaked
Legal Counsel at ironSource
“What I like best about Sanction Scanner is its real-time screening capability and automated alerts. It helps us detect potential matches instantly and take immediate action, which is critical for our AML compliance.”

Tolgahan Kapanci
Head of Compliance at PeP
“With Sanction Scanner, we offer a fast, easy, and secure customer onboarding process. Thanks to its enhanced scanning tool, we focus on real risks, not false positives. Thus, we can meet our AML obligations and our customers' expectations.”

Arda Akay
Chief Compliance Officer at Tom Bank
“Sanction Scanner provided us the most comprehensive database to screen our clients. It includes lists from all over the world and is always up-to-date.”

Gulnihal Akartepe
Global Vice President at TPAY
“With Sanction Scanner, we reduce the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing by controlling on local and international lists also to avoid risks during our onboarding process.”

Oğuzhan Akın
Experienced Banking & Expansion Manager (MEA) at WİSE





Customer Risk Assessment
Customer Risk Assessment refers to evaluating the probability of each customer being involved in money laundering or illicit financial activities. This entails evaluating the type of business, location, patterns of transactions, and the origin of funds. Considering all these factors, the CRA module of Sanction Scanner calculates and adjusts risk scores dynamically, and maintains constant updates to customer information.
It allows entities to apply appropriate due diligence, allocate compliance funds optimally, and satisfy all the conditions set under AML laws. With Sanction Scanner, financial organizations seamlessly spot high-risk customers, perform Enhanced Due Diligence, and ensure alignment with the AMLD standards of FATF and the EU.
In most cases the type of customer, country of the customer, pattern of transactions, origin of funds, business sector, and any PEP affiliation are all considered when assessing risk. With the help of configurable fields and risk based external data sources (databases of sanctions and PEPs) Sanction Scanner provides accurate scores.
Customers are broadly categorized into three distinct risk levels: low, medium, and high. This classification considers a customer's risk geography, the industry they operate in, the volume of transactions, and any potential exposure to sanctions. Sanction Scanner's dashboard helps teams monitor and prioritize cases by visualizing risk levels in real-time.
Due diligence is influenced greatly by the risk level attributed to a customer. Sanction Scanner streamlines the process by filing customers under Simplified Due Diligence and Enhanced Due Diligence based on the customer's active risk profile.
Absolutely, risk levels can change if a customer's activity, geography, or ownership changes. Ongoing monitoring helps Sanction Scanner refine the customer profile and keeps risk scores accurate to real-world changes.
Automation cuts down on repeated tasks, lessening the strain of manual workload. Sanction Scanner uses automation to score customer risk, provides AI-powered risk assessments, and dynamically updates risk assessments and scores in real-time if risk changes.
Dynamic risk scoring is the automated process of updating the customer's risk levels.
With Sanction Scanner's dynamic rule engine, Compliance Officers can define thresholds and scenarios in countless ways, building rules as naturally as writing a sentence.
Outdated assessments can lead to penalties, compliance cases and reputational damage easily. Sanction Scanner minimizes these exposures with automated scoring, reassessment, and risk level change alerts.
For customer risk assessment, Sanction Scanner offers real-time risk scoring, risk frameworks that align with country-specific AML regulations, and integrated transaction monitoring. We offer customizable models, real time monitoring and automated system to monitor updates
Yes. FATF and local regulators require a risk-based approach—making individual customer risk assessment a core AML obligation.
Yes. You can define risk rules by region, industry, or behavior to tailor assessments to your internal risk appetite.
Absolutely. Our APIs allow seamless embedding into onboarding flows, CRMs, or AML back offices for real-time decision support.
By assigning dynamic risk levels, Sanction Scanner helps prioritize which customers require more frequent reviews, enhanced due diligence, or tighter transaction monitoring. This enables teams to focus on high-risk clients without overwhelming resources on low-risk ones.




