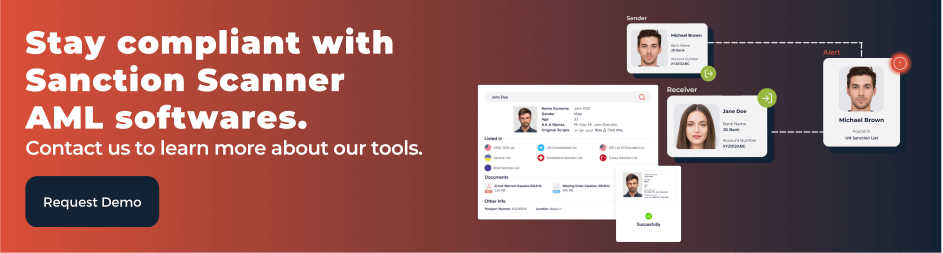
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) includes policies, laws, and regulations to prevent criminals' financial crimes and illegal activity. Global and local regulators are established worldwide to prevent financial crimes and criminal activities, and these regulators build policies. Companies must comply with these regulations, even though compliance can be complex. As a result, financial organizations have compliance departments and buy software solutions.
What is Anti Money Laundering (AML)?
In the most general sense, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to the collection of laws, law enforcement, processes, and regulations that prevent illegally obtained money from entering the financial system.
AML targets a wide variety of crimes, from corruption and tax fraud to market manipulation and illicit trade and financing of terrorism, as well as efforts to mask these activities as the source of money.
Because most criminals and terrorists rely significantly on laundered money for their illegal operations, having effective AML procedures in place has broader crime-reducing consequences.
Many businesses must do extensive customer due diligence under Money Laundering Regulations to prevent money laundering and economic crime. AML checks are essential to customer due diligence since they screen clients against PEP and Sanctions lists and verify their claimed identities. Failure to comply with AML standards can result in financial penalties and, in extreme cases, disqualification as a business/director.
Who is Using Anti Money Laundering (AML)?
Financial institutions are the most prominent users of AML legislation, as they are compelled to report any suspicious behavior to authorities. However, financial institutions are not only obligated to report suspicious behavior. Still, they are also at a higher risk of money laundering since they provide credit to consumers who open accounts with the company.
History of Anti Money Laundering (AML)
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), established in the United States in 1970, was a pioneering piece of legislation in the fight against money laundering. It has been continually updated and strengthened, with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) currently in charge of its administration.
In 1989, the Global Financial Action Task Force (FATF) was formed by a group of governments and organizations. Its mission was to develop and promote international standards for preventing money laundering. After the 9/11 attacks, the FATF expanded its focus to include anti-money laundering (AML) and terrorism financing.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF), with its 189 member countries, also plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the global monetary system. It is particularly concerned about the impact of money laundering and similar crimes on the integrity and stability of the financial sector and the broader economy.
In 1990, the European Union introduced its first anti-money laundering Directive. This directive, which is regularly updated, aims to prevent the misuse of the financial system for money laundering.
In the UK, anti-money laundering laws are enforced under the Proceeds of Crime Act 2002 (POCA). Several organizations, including the NCA, SFO, FCA, and HMT, work together to prevent financial crime. Despite leaving the EU, the UK's laws and regulations still align with the FATF recommendations and the EU's Anti-Money Laundering acts.
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) in the USA develops programs to safeguard U.S. foreign policy and national interests. Many other countries have regulatory bodies that adhere to FATF regulations.
What Is AML Compliance?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance lies at the forefront of maintaining the integrity of the global financial system. It consists of laws, regulations, and internal controls that regulated institutions and persons must implement in order to discourage and detect money laundering, financing of terrorism, and other money laundering-related financial crimes.
According to our experts, AML compliance is so much more than simply box ticking to appease regulators. It is an active defense against the misuse of financial systems for illicit ends. Without it, criminal groups would be able to openly use financial institutions to launder the proceeds of illegal activities.
What Does AML Compliance Software Do?
AML compliance solution is a specialized technology tool that is tailored to automate and make the process of identifying suspicious transactions easier. Financial institutions use such platforms to monitor transactions, scrutinize customer data, and assess risk against global AML norms.
These solutions typically provide such functionalities as customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, sanctions and PEP screening, and reporting for regulatory compliance. By automating these processes, AML solutions reduce the scope for human error and enhance process efficiency. In our opinion, such programs are now inevitable and not voluntary. With the growing volumes of financial transactions and more advanced techniques of laundering, manual surveillance is no longer a possibility.
How Does AML Compliance Work?
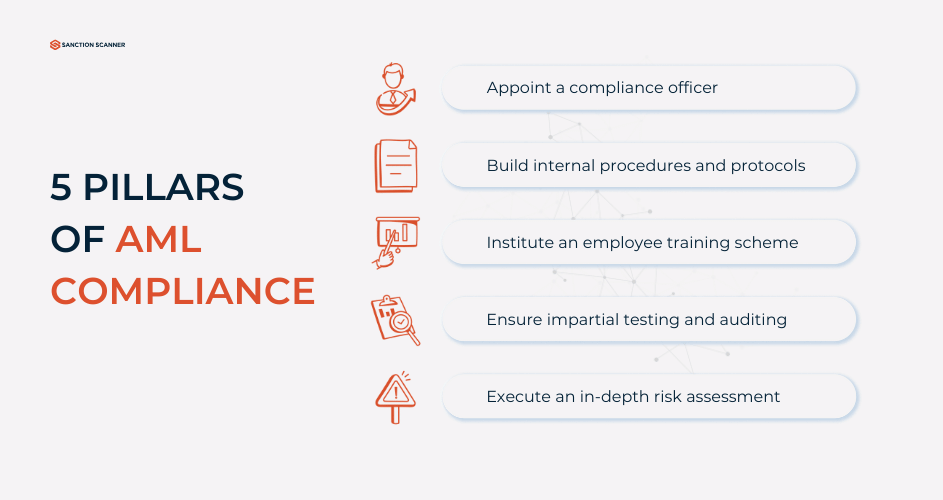
AML compliance works through organized, risk-based programs that are adjusted to the institution's size, services, and level of exposure. These programs are based on four key components: due diligence, monitoring, reporting, and internal control.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
CDD is the pillar of every successful AML program. It is the policy requirement that calls for the affirmation of clients' identity and understanding the nature of business relationships. It involves collecting government IDs, address proof, and identification of beneficial owners, where it is about legal persons. Organizations have to assign risk profiles to each client and make the necessary revisions on a regular basis. According to the AML experts, ongoing CDD not only meets the requirements of the law but also serves as a step against strategic financial abuse.
Transaction Monitoring
After the clients are onboarded, their financial behavior must be closely monitored. Advanced systems track account activity and measure it against known patterns of behavior. They flag up anomalies—big-speed fund transfers between jurisdictions, massive cash deposits, or out-of-profile transactions. Next-generation transaction monitoring systems are leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to reduce false positives and improve accuracy. We believe that such implementation of smart automation here represents a paradigm shift in how banks approach detecting financial crime.
Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
When suspicious systems detect a possible illegal transaction, the institution must file a Suspicious Activity Report with the concerned authority. SARs play a crucial role in criminal investigations since they provide regulators and law enforcement agents with valuable tips. In order to meet regulatory requirements, these reports have to be accurate, detailed, and submitted within specific time frames. Failing to do so can attract legal and financial implications.
Risk Assessment and Internal Controls
All institutions must regularly review their risk exposure to financial crime. It entails the study of customer categories, product portfolios, geographic risk, and transactional patterns. Through these, firms must implement policies and controls that will manage those risks. Internal controls also include training of staff, enhanced high-risk customer due diligence, audit trails, and secure data handling. These, in my opinion, are what put AML into practice from theory.
Why is AML Compliance Important?
The amount of money laundered globally in one year is believed to be 2% to 5% of global GDP, or $800 billion to $2 trillion - and this is a low estimate. Money laundering is frequently associated with illegal arms sales, smuggling, embezzlement, insider trading, bribery, and computer fraud schemes. It's also widespread in organized crime, such as human trafficking, weapons or drug trafficking, and prostitution rings.
Counter-funding of terrorism (CFT), which financial institutions utilize to combat terrorist financing, is closely tied to anti-money laundering. Money laundering (source of funds) and terrorism financing are both addressed by AML legislation (destination of funds).
Aside from the moral duty to combat money laundering and terrorist financing, financial institutions use AML tactics for the following reasons:
- Compliance with regulations requires them to monitor consumers and transactions and report questionable activities.
- Protection of their brand's reputation and shareholder worth.
- Avoidance of consent orders and potential civil and criminal fines for disobedience or negligence.
- Cost savings from fines, staff, IT expenditures, and funds set aside for risk exposure.
List of Global AML Regulations and Regulatory Authorities by Country
| Country | Regulator(s) | Regulation(s) |
| United States | FinCEN | Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), USA PATRIOT Act |
| United Kingdom | FCA, HMRC, National Crime Agency (NCA) | Money Laundering Regulations 2017 (amended), Proceeds of Crime Act (POCA) |
| Canada | FINTRAC | Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act (PCMLTFA) |
| Singapore | Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) | MAS Notice 626, AML/CFT Guidelines |
| Australia | AUSTRAC | Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Act 2006 |
| India | FIU-IND, RBI, SEBI, IRDAI | Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), RBI AML Guidelines, SEBI, IRDAI |
| UAE | CBUAE, Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) | Federal Decree Law No. 20 of 2018 |
| Germany | BaFin | German Money Laundering Act (GwG), EU 6AMLD |
| France | ACPR, TRACFIN | French Monetary and Financial Code, EU 6AMLD |
| Netherlands | De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB), FIU-NL | Wwft (Dutch AML Act), EU 6AMLD |
| Hong Kong | HKMA, SFC, C&ED | Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Ordinance (AMLO) |
| Japan | JFSA, National Police Agency (NPA) | Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds |
| Switzerland | FINMA | Anti-Money Laundering Act (AMLA) |
| South Africa | Financial Intelligence Centre (FIC) | Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA) |
| Brazil | COAF (Council for Financial Activities Control), Banco Central | Law No. 9,613/1998 |
| Mexico | CNBV | Federal Law for the Prevention and Identification of Operations with Illicit Resources |
| Saudi Arabia | Saudi Arabia Financial Intelligence Unit (SAFIU), Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) | Anti-Money Laundering Law (2017, updated) |
| Türkiye | MASAK | Law No. 5549 on Prevention of Laundering Proceeds of Crime |
Definition of Well Known Regulations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF): The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global standard-setter in AML. It has 40 Recommendations ranging from CDD to cross-border collaboration. Failure by countries to implement them will land them on a blacklist, which can greatly reduce their access to the global financial markets.
EU 6AMLD: The European Union's 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directive expands on previous legislation with tougher penalties, wider criminal liability, and measures to address existing threats like cybercrime. It also requires a harmonized approach to AML in the entire EU member states.
FinCEN (United States): In the United States, Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) compliance is enforced by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). Institutions must maintain records of transactions, file suspicious activity reports, and implement customer identification procedures.
Crypto Regulations: Cryptocurrencies added an additional layer of complexity to AML compliance. FATF and FinCEN now require crypto exchanges and wallet providers to perform KYC, monitor transactions, and report suspicious transactions. To my understanding, these regulations are necessary for including crypto in the formal financial system safely.
What Should Required Entities Do To Comply With AML Regulations?
When developing procedures for detecting money laundering activities within their scope, obligated entities (a list of which may be found here) are held to high standards. To comply with primary AML national and international legislation, they must build a complete AML framework that includes the following measures:
- Mechanisms for screening transactions and software filters;
- Strong Know Your Consumers (KYC) methods to verify, identify, and check customers or businesses against sanctions and watchlists;
- Identification of ultimate beneficiaries for legal companies through due diligence and enhanced due diligence based on the level of assessed risk;
- Demonstrate that the business took every effort to avoid money laundering-related actions.
- Preserve all documentation pertaining to the identification of its clients and transactions.
Compliance with AML legislation for "chosen obligated entities" posing a high risk will be monitored in the near future by the forthcoming European entity, AMLA EU (Anti-Money Laundering Authority of the European Union). As a result, a stronger emphasis on such institutions may significantly influence their requirement for AML compliance.
What are the Stages of AML?
AML standards vary by country, but in general, financial institutions take the following steps to ensure compliance:
Know Your Customer (KYC)
To maintain authenticity, financial institutions need sufficient client identity and verification. Higher-risk goods and services necessitate more detailed documentation.
Reporting on Large Money Transactions
Institutions must file a regulatory report (known as a "CTR" in the United States) for transactions over a specific threshold made by a single client during a business day.
Monitoring and Reporting of Suspicious Actions
Regulatory bodies issue AML guidelines outlining the types of activity that should be monitored (e.g., making numerous cash deposits or withdrawals over several days to avoid a reporting threshold). If an AML investigator discovers behavior that exceeds reporting criteria and has no obvious business purpose, they must submit a SAR/STR with the FIU in order to meet regulatory obligations.
Compliance With Sanctions
Financial institutions are required by regulatory bodies such as the US Treasury Department, the US Office of Foreign Assets Control, the United Nations, the European Union, Her Majesty's Treasury, and the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering to check transaction parties against lists of sanctioned individuals, companies, institutions, and countries.
What Are the Consequences for Businesses That Fail to Execute a Compliant AML Process?
In recent years, there has been an increase in investigations conducted by relevant national agencies for AML standards breaches. As a result, businesses that failed to develop a strong AML program and did not demonstrate adequate monitoring were fined. Their scope and prerogatives may change depending on the authority.
For example, the French institution Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution (ACPR), which is in charge of supervising bank and insurance activities, has the authority to impose the following sanctions:
- A fine of up to EUR 100 million, or 10% of turnover;
- Withdraw the company's financial license, enabling it to operate on the French market;
- Interdict an individual from working in the financial industry;
- Appoint a non-permanent administrator for monitoring.
Other instances may demonstrate severe penalties for failure to comply with AML rules. For example, the British regulator Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), penalized the German Commerzbank's London branch GBP 37 million in June 2020 “for failing to put adequate AML systems and controls in place between October 2012 and September 2017.”
What is an AML Program?
An AML program is a set of procedures and policies designed by financial institutions to prevent, detect, and report money laundering and terrorism financing activities. It includes conducting risk assessments, implementing CDD measures, ongoing monitoring of transactions and staff training, and ensuring compliance with both national and international regulations to combat financial crimes.
Key AML Acts
At the heart of the anti-money laundering efforts are several pivotal AML Acts that have been adopted worldwide to ensure a robust defense against the laundering of illicit funds. Here's a breakdown of key legislations:
- The Bank Secrecy Act (1970), USA: Often considered the original AML legislation, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) requires financial institutions in the United States to assist U.S. government agencies in detecting and preventing money laundering.
- The Money Laundering Control Act (1986), USA: This Act established money laundering as a federal crime independent of the underlying criminal activity generating the money. It emphasized the importance of knowing the customer to prevent these illicit activities.
- The Patriot Act (2001), USA: Enacted after the September 11 terrorist attacks, the Patriot Act expanded the scope of the BSA to include terrorist financing. It introduced stricter regulations, including the requirement for financial institutions to develop AML programs and enhanced the due diligence processes.
- The Proceeds of Crime Act (2002), UK: POCA provides the legal framework for the recovery of proceeds from crime in the UK. It includes provisions for the confiscation of assets in criminal cases, civil recovery of the proceeds of crime, and the imposition of money laundering offences.
- The Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD), EU (2020): 6AMLD represents a crucial step forward in the EU's fight against money laundering and terrorism financing. It broadens the scope of existing laws, clarifying and standardizing the definition of money laundering across member states. Furthermore, it extends criminal liability to legal persons (e.g., corporations), enhances cooperation between EU countries, and lists 22 predicate offenses associated with money laundering, ensuring a more comprehensive approach. Notably, it imposes tougher penalties, with a minimum of four years of imprisonment for money laundering offenses, thus signaling the EU's intensified resolve to combat financial crimes.
Each of these acts contributes to a global infrastructure aimed at making it increasingly difficult for criminals to launder money and finance terrorism. They reinforce the need for financial institutions to establish robust compliance programs that include CDD, transaction monitoring, and the reporting of suspicious activities.
AML in the Cryptocurrency Industry
Anti-money laundering (AML) in the cryptocurrency industry refers to the measures taken to prevent cryptocurrencies from being used to facilitate money laundering and other illicit activities.
To prevent money laundering through the use of cryptocurrencies, exchanges and other companies in the cryptocurrency industry may implement AML policies and procedures, such as verifying the identities of their customers and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity. In addition, some countries have also introduced regulations that require cryptocurrency companies to comply with AML laws and report suspicious activity to the relevant authorities.
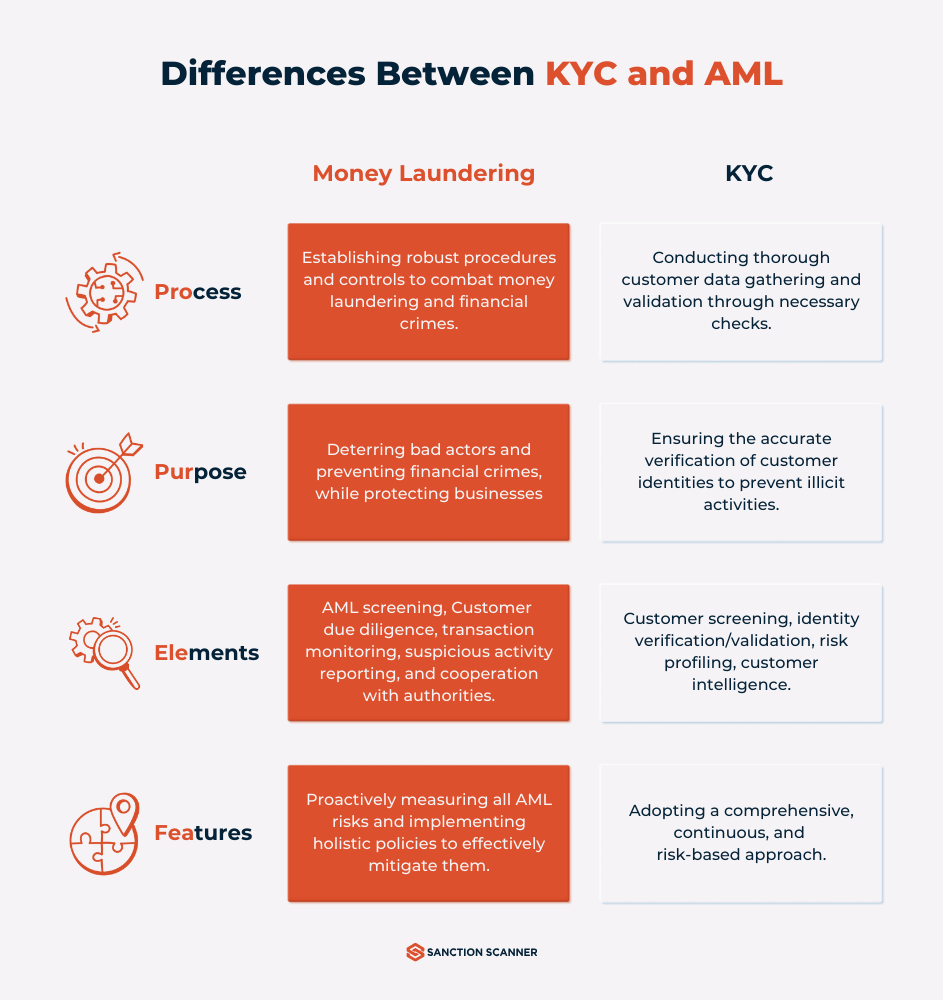
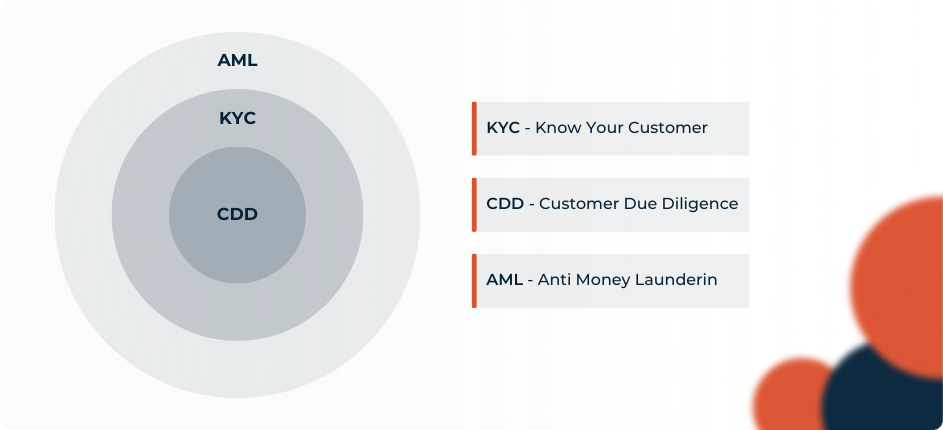
What Is the Difference Between AML, CDD, and KYC?
Customer due diligence (CDD) refers to the inspection that financial institutions (and others) are expected to carry out to prevent, identify, and report violations. Anti-money laundering (AML) is the general term for the laws, rules, and processes that prevent money laundering. Customer due diligence is applied to screening and validating prospective clients under Know Your Client (KYC) standards.
Sanction Scanner's AML Solutions
Criminals find new ways to launder money as technology advances. Businesses should use more advanced tools to fight against financial crimes and terrorist funding. Sanction Scanner's solutions are developed to protect companies from financial crimes. Compliance software has simplified complex AML compliance processes for companies. AML compliance is no longer voluntary—it's a strategic imperative. In our opinion, companies that treat compliance as a business challenge rather than a regulatory nuisance won't only avoid fines but also build long-term trust with clients and regulators.
With changing threats and growing regulation, institutions require tools like Sanction Scanner. We convert AML compliance from a static task into an intelligent, dynamic process that enables institutions to stay safe and competitive.
Sanction Scanner's database consists of over up-to-date global 3000 Sanctions lists, PEP lists, and Adverse Media Data. Therefore, you can integrate Sanction Scanner into your compliance program easily. You can contact us if you need more information about Sanction Scanner solutions.
FAQ's Blog Post
AML refers to laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. It applies across banking, fintech, and other high-risk sectors.
It helps protect the financial system from abuse by criminals and terrorists. Strong AML controls also build trust with regulators and customers.
Key frameworks include the FATF Recommendations, the EU AML Directives, and the USA PATRIOT Act. Many countries adapt these to their own regulations.
Financial institutions, fintechs, DNFBPs, and other regulated businesses must implement AML programs. Compliance officers oversee day-to-day adherence.
KYC is a part of AML that focuses on verifying customer identity. AML is broader, covering detection, monitoring, and reporting of suspicious activities.
They include customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, and suspicious activity reporting. These processes work together to detect illicit finance.
A SAR is a document submitted to regulators when a transaction appears linked to illegal activity. Filing is mandatory for regulated businesses.
Politically Exposed Persons are individuals with high-profile public roles who may pose higher corruption risks. AML programs require enhanced due diligence for PEPs.
Placement, layering, and integration. Each stage hides the origin of illicit funds more effectively.
The Financial Action Task Force sets global AML/CFT standards and evaluates countries’ compliance. Its recommendations shape national AML laws.
Penalties include heavy fines, license revocation, and criminal charges. Reputational damage can also be severe.
Banking, fintech, cryptocurrency exchanges, casinos, real estate, and legal services are heavily regulated. These sectors face higher financial crime risks.
AI, machine learning, and blockchain analytics improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives. Automation also lowers compliance costs.
It is the continuous review of customer transactions and profiles to detect changes in risk. This helps catch suspicious activity in real time.