AML Solutions For
Crypto Exchanges
AML compliance is easier than ever for the Crypto Industry

TRUSTED BY OVER 800+ CLIENTS
We bring solutions that will make it easier for our customers to comply with AML Regulations.








Don't risk your reputation.
People use crypto exchanges to deposit and store their money. Thus, Crypto exchanges have to implement AML rules and controls like other financial institutions. The powerful API support of Sanction Scanner automates the AML compliance processes of crypto exchanges.

Reduce False Positives from Onboarding to Trading
Your customer might hesitate when their registration process or transactions stop for eligibility during short trading. Sanction Scanner's powerful and flexible APIs reduce false positives and manual operations so you can give a smooth experience to your customers. You can give a smooth experience to your customers with Sanction Scanner's powerful and flexible APIs.
“Sanction Scanner's software is easy to use, and we enjoy working with it. Since implementing its solution, we have significantly reduced false positives. The time and effort we previously spent on false positive alarms can now be directed towards other aspects of the business, which contributes to its growth.”

Guy Shaked
Legal Counsel at ironSource
“What I like best about Sanction Scanner is its real-time screening capability and automated alerts. It helps us detect potential matches instantly and take immediate action, which is critical for our AML compliance.”

Tolgahan Kapanci
Head of Compliance at PeP
“With Sanction Scanner, we offer a fast, easy, and secure customer onboarding process. Thanks to its enhanced scanning tool, we focus on real risks, not false positives. Thus, we can meet our AML obligations and our customers' expectations.”

Arda Akay
Chief Compliance Officer at Tom Bank
“Sanction Scanner provided us the most comprehensive database to screen our clients. It includes lists from all over the world and is always up-to-date.”

Gulnihal Akartepe
Global Vice President at TPAY
“With Sanction Scanner, we reduce the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing by controlling on local and international lists also to avoid risks during our onboarding process.”

Oğuzhan Akın
Experienced Banking & Expansion Manager (MEA) at WİSE
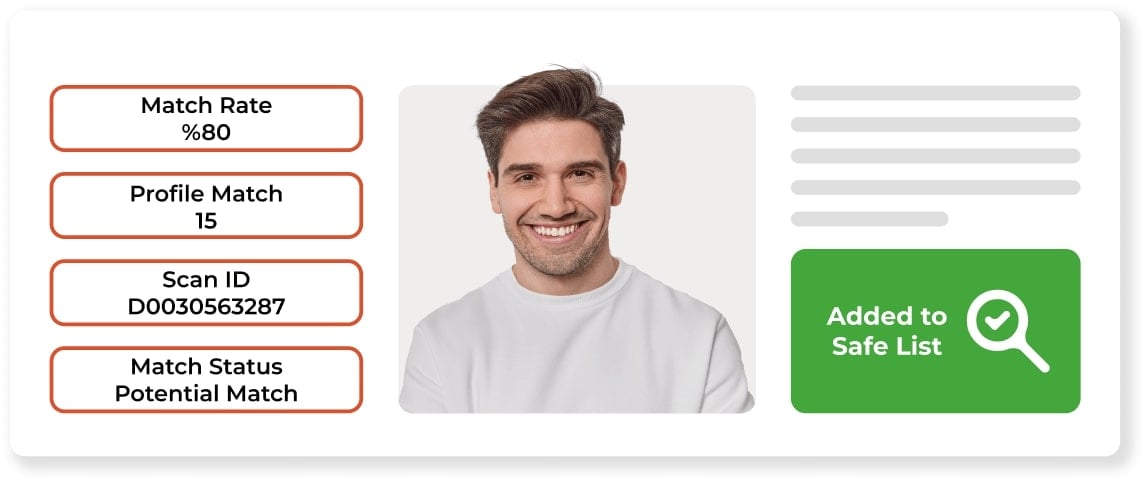








Get Ready for AML Regulations Today
Countries started to take action to protect the crypto market from financial crimes. The crypto companies face challenges more than ever with the new laws. They have to implement some of the rules other financial institutions have for years.



AML Screening Software for Crypto Industry
Organizations in the crypto industry must fulfill their AML and KYC obligations during account opening for their customers. Businesses can scan their customers in more than two hundred countries' sanctions, PEP, and Adverse Media data to avoid AML penalties using our AML Screening Software.
FAQs about Crypto
Yes. Crypto exchanges, wallets, and DeFi platforms must follow AML laws, including KYC, transaction monitoring, and sanctions screening to prevent financial crime.
The Travel Rule requires crypto firms to share sender and receiver info for large transfers, aligning with FATF standards and increasing transparency in transactions.
They use tools like real-time ID checks, biometrics, and document verification to confirm user identity, flag risks, and meet regulatory requirements.
Red flags include high-volume mixing, use of privacy coins, structuring, and transfers to/from high-risk jurisdictions with weak AML oversight.
They rely on blockchain analytics, anomaly detection, and wallet behavior monitoring. Sanction Scanner supports this with risk scoring and real-time alerts.
Yes. Platforms must screen users, wallets, and smart contracts against OFAC, UN, and EU lists. Real-time screening is critical for compliance.
Penalties include fines, loss of licenses, reputational harm, banking restrictions, and global market exclusion due to regulatory non-compliance.
Yes, partially. Many DeFi projects now adopt compliance tools or partner with KYC/AML providers to meet emerging regulatory expectations.
Blockchain analytics helps trace fund origins, flag risky wallets, and detect illicit activity. It’s essential for effective crypto AML programs.
Yes. Sanction Scanner offers API-based integration for KYC, wallet screening, and monitoring—ideal for CEXs, DeFi, and NFT platforms.
Yes. NFT platforms may be subject to AML rules, especially if they enable large-value transactions or fiat-to-crypto conversions. KYC and wallet screening are recommended.
A high-risk wallet is one linked to illicit activity, such as darknet markets, sanctioned entities, or mixers. These are flagged through blockchain analytics and risk scoring.
Not all wallets require KYC. However, custodial wallets and exchanges are typically obligated to verify user identity under AML laws in most jurisdictions.
Authorities use blockchain analytics tools to trace transactions, identify connections to flagged addresses, and collaborate with crypto compliance providers to monitor flows.
Mixers are legal in some jurisdictions but often raise AML concerns due to their anonymity features. Use of mixers may trigger Enhanced Due Diligence or regulatory scrutiny.
KYT refers to the process of monitoring and analyzing transactions in real time to detect suspicious patterns, risk levels, and potential financial crime activity.
Yes. Transactions involving stablecoins are monitored under AML frameworks, particularly when used on regulated platforms or for cross-border value transfer.
EDD involves verifying source of funds, increased monitoring, and enhanced identity checks. High-risk factors may include large volume trading, offshore accounts, or PEP status.
It’s a risk rating assigned to a wallet or address based on transaction history, counterparties, and linkages to known threats. Sanction Scanner provides real-time scoring.
Yes. Some jurisdictions now require screening of smart contracts to ensure they are not facilitating illicit transactions or interacting with blacklisted wallets.



