Money laundering disguises the origins of illegal income by means of making it seem as though they came from a legitimate commercial enterprise. Criminals put it to use in this kind of way that they can indulge in their profits without running afoul of the law. But this is not just a sneaky backroom technique it's a international phenomenon that fuels crime, corruption, or even terror. Let us speak about how and why it occurs, who does it, how it's miles evolving, and what we will all do to forestall it.
What is the Meaning of Money Laundering?
Money laundering is an illegal act in which large amounts of money are used to conduct criminal activities in drug trafficking, terrorism, or any other corruption. It is a threat to the global financial system and a serious risk to market integrity. This article is a guide that highlights the three stages of money laundering which are placement, layering, and lastly integration.
Real world example: The United Nations believes that the 2% to 5% of world GDP (1.5 - 2 trillion dollars yearly) is laundered worldwide.
Why is Preventing Money Laundering Important?
First of all, money laundering decreases the trust in financial institutions by manipulating the markets, enabling illicit funds to flow into legitimate financial systems and tax evasions. Moreover, money laundering is not only connected to financial crime groups, but also stems from such illegal activities as terrorism, drug trafficking, and human trafficking. Thus, preventing money laundering stops these kinds of crimes as well.
Most of the time, money laundering becomes the main reliance for terrorist organizations to endanger national and international security, which makes the prevention inevitable to maintain global security. On top of these, the failure of countries and institutions to control money laundering harms their reputation, makes it hard for them to attract investments, and results in being greylisted by institutions like FATF.
Finally, stopping money laundering is definitely a must to avoid legal punishments and heavy fines due to legal obligations.
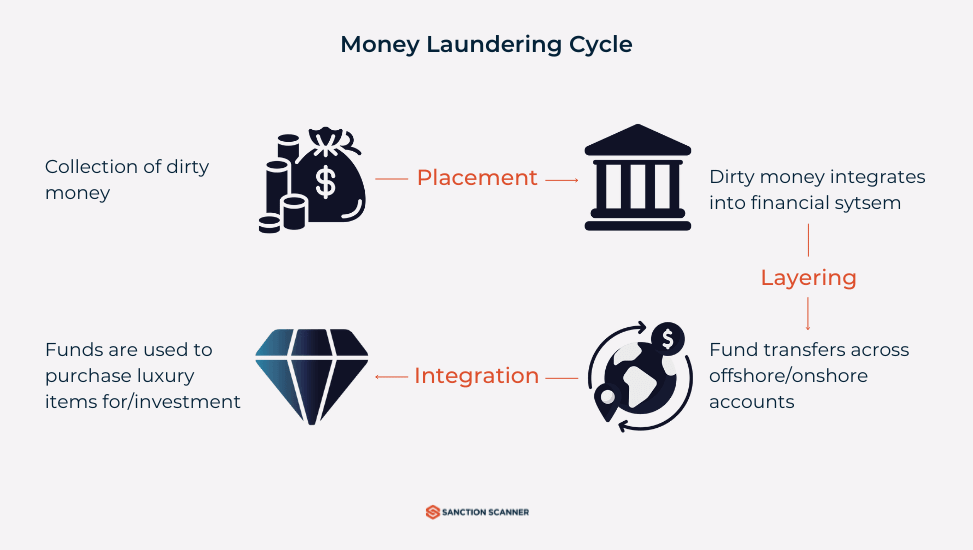
How Does Money Laundering Work? The 3 Stages of ML
Stage One: Placement
The laundering process begins with placement. That is when criminals deposit their illegal money into the economy. Think of it as the point when dirty money tries to blend in with clean money. It's also the riskiest move for criminals because authorities closely monitor the first wave of large cash sums. That is why they use various tactics to make those transactions seem ordinary.
Instead of making big deposits all at once, they shape it into numerous smaller transactions—a procedure known as structuring or smurfing. Others will discover a more oblique path, like shopping for precious items together with artwork or earrings, or putting bets at casinos wherein winnings are considered valid earnings. Real property is also appealing because it permits big amounts of money to switch with minimal monitoring. This stage demonstrates the manner in which financial systems are exploited when there is no strong defensive system established. This also indicates the reasons why compliance teams need products that trigger alarms for unusual deposits or unconventional asset purchases early on.
Recent Example: In 2023, a big money laundering cartel used real estate purchases in Canada to launder over CAD 45 million of proceeds of crime.
Common Methods of Placement
- Cash Deposits: Criminals deposit small amounts of cash into different bank accounts and they keep the amount just below reporting thresholds. Their goal is to get away from detection. This whole process is called “smurfing” or structured deposits.
- Use of Casinos: The second method is to gamble and cash out the winnings so that it looks as if it is legitimate income. That is why casinos must be specifically targeted due to the high volume of cash circulated in this sector.
- Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML): Another way to funnel funds is by receiving invoices for goods that are over or undervalued. This allows criminals to hide the circulation of their illicit funds by making them look as if they are part of a legitimate trading activity.
Risk Indicators of Placement
- Financial profiles or stated goals that do not align with withdrawals or cash deposits
- Frequent cashing out winnings from casinos or owning luxury goods
- Profiles involved in sudden transactions involving high-risk industries
How Can Sanction Scanner Help Detect Placement Activities?
Such unusual transactions are efficiently exposed and completely blocked by the Sanction Scanner’s Transaction Screening Tool. Whether it is flagged accounts or unusual deposits in high-risk industries, our compliance teams identify illegal attempts with high accuracy. Some of the services we offer include:
- Identifying suspicious cash activity that does not align with client profiles
- Scrutinizing transactions in high-risk sectors such as casinos, real estate, and cryptocurrency
- Generating audit-ready SARs (Suspicious Activity Reports)
Stage Two: Layering
After the money is within the system, the second objective is to disconnect it from its criminal source. The second phase is known as layering. During this phase, criminals insert the money into a tangled web of transactions so that the source of the funds is concealed. Whereas placement conceals the entry of the money, layering confuses its path.
During this stage, money launderers would be able to move illicit funds via multiple accounts in different countries. Offshore jurisdictions are often utilized because their loose regulation and secrecy laws make tracing operations very difficult. Some criminals take their activities as far as converting money into virtual currency or other digital assets, which offer more anonymity. Shell companies, fictitious invoices, and forged trade documents are regular tools. They present the transaction in a legitimate light while concealing the money trail. This phase is an actual challenge for law enforcement and technology. Without advanced analytics and cross-border cooperation, it is nearly impossible to track these funds.
Common Methods of Layering
- Offshore Transfers: One of the most common practices is to move funds through multiple international accounts. Countries known to be tax havens with limited jurisdictions are the locations that give criminals anonymity to conduct illegal activities.
- Crypto Mixing Services: As cryptocurrencies are used in mixing platforms, financial authorities might have difficulty in detecting the source of transactions. Criminals choose this method to obscure the sender and recipient interaction, and they erase digital trails.
- Shell Companies: Another method is to form a corporation or a company through which illicit funds are funneled through seemingly legitimate transactions.
Risk Indicators of Layering
- Frequent transfers in countries known for weak anti-money laundering regulations
- Customers with normal business activities but extremely complicated transaction patterns
- Unclear business purposes or crypto-related transactions, sudden spikes
How Can Sanction Scanner Help Detect Layering Activities?
Sanction Scanner’s Transaction Monitoring System offers a tool that can effectively detect unusual transactions across borders. With advanced analytics and security alerts, we offer institutions the ability to identify and flag suspicious layering activities. Sanction Scanner integrates a strong compliance infrastructure with instant alerts and coherent risk scores that will certainly reduce the risk of money laundering. Some of the services we offer include:
- Analyzing cross-border transactions, specifically locations with limited jurisdictions
- Detecting behavioral anomalies in user profiles
- Screening money exchanges, crypto-related transactions, and other suspicious digital trails.
Stage Three: Integration
The last stage is to make their illegal activities appear as if the money is earned legally. At this final stage, the money appears to be “clean” so criminals either invest in legitimate businesses, real estate, or other seemingly high-value and lawful ventures.
It is a must to understand these three stages so that the criminal organizations and their illicit operations can easily be suspended by AML detection mechanisms.
Common Methods of Integration
- Real Estate Investments: This includes investing in high-value properties.
- Real Estate Over-Invoicing: Inflated property values are another method to disguise illicit funds.
- Cross-Border Transfers: Fake or shell companies are used to conduct international money transfers.
- Crypto Wallet Splitting: Breaking funds into smaller pieces and sending them to many different cryptocurrency wallets is another method.
- Business Ventures: Real businesses with a cash-intensive nature like restaurants or construction companies, are also used.
- Luxury Asset Purchases: High-value and luxury assets are used to transfer money internationally.
Risk Indicators of Integration
- High-value asset purchases that do not align with the customer’s profile
- Inconsistent patterns of investment that appear unusual for the individual’s profile
- Sudden increase in wealth or unexplained financial activity that lacks a clear source of income
How Can Sanction Scanner Help Detect Integration Activities?
Money laundering schemes are becoming increasingly complicated, and they evolve rapidly in response to regulatory scrutiny. Sanction Scanner’s Ongoing Monitoring Tool provides high-profile techniques and real-world implications for detecting integration activities. Our professional system consistently monitors irregular behavior patterns. Some of the services we offer include:
- Analyzing transactional data to identify red flags
- Conducting PEP screening, media monitoring and automated compliance reporting
- Monitoring of high-risk locations known for integration activities
Types of Money Launderers
You might suppose only mafia dons or narcotics barons have a hand in this kind of economic fraud. But in reality, the players are far wider in scope. Some perform solo, corrupt politicians, con artists, or high-ranking narcotics sellers. They lead conspicuous consumption, shopping for imported motors, mansions, and dressmaker objects on cash that technically shouldn't be there of their recorded earnings. One thing we’ve noticed is that corrupt officials, especially, use laundered money to entrench their power. They use wealth to manipulate others and secure loyalty, fueling a vicious cycle of control and corruption.
Sometimes whole groups are at stake - knowingly or through inattention. Offshore accounts, shell corporations, and even valid corporations grow to be channels of washing money laundering. The Panama Papers scandal discovered how international regulatory firms and specialists helped rich customers hide their assets using offshore structures. These systems have now not only tax-saving sports - they also enable mass-scale cash laundering. When professionals like accountants and lawyers enable laundering (accidentally or intentionally), it raises difficult ethical and regulatory questions. Who's ultimately responsible?
List of potential money launderers;
• Drug traffickers
• Corrupt politicians
• Fraudsters and scammers
• Human traffickers
• Arms dealers
• Terror financiers
• Organized crime leaders
• Shell companies
• Offshore structures
• Major corporations (knowingly or not)
• Law firms (setting up offshore accounts)
• Accountants and financial advisors
What Are the Main Techniques of Money Laundering?
Criminals have grown smarter, and so have their methods. Here are some of the most common ways they clean their dirty money:
Smurfing
This method involves breaking down big chunks of illegal cash into smaller pieces and depositing them little by little into different accounts. Criminals use multiple people, called “smurfs” to avoid triggering any alarms at the bank. Smurfing works because financial institutions are often required to report large or suspicious transactions. By keeping deposits below those thresholds, criminals hope to slip under the radar.
Structuring
Structuring is basically smurfing with a schedule. Instead of dumping all the money in at once, criminals spread deposits out over time. For example, they could deposit $9,000 nowadays, any other $9,000 subsequent week, and so forth. This trick exploits banking laws that require reports on transactions over a sure amount - often $10,000. By staying simply below that line, they keep away from detection.
Trade-Based Laundering
Criminals also hide money in fake or exaggerated trade deals. They might overvalue or undervalue shipments, falsify invoices, or move non-existent products. Because international trade involves a lot of paperwork and cross-border complexity, it’s a goldmine for money launderers. And here’s the catch - these fake trades can be really hard to detect, especially when they involve multiple countries, currencies, and customs agencies.
Shell Companies
Shell companies are fake businesses with no real operations. On paper, they look legit. But in reality, they’re just empty shells used to move money around. Criminals use these companies to mix dirty money with clean profits, making the origin of the funds harder to trace. Often, these shell entities are set up in countries with loose regulations, making investigations even tougher.
Cryptocurrency Laundering
Digital currencies like Bitcoin opened a new door for money laundering. Because crypto is often anonymous and decentralized, criminals love it. They use “mixers” or “tumblers” to shuffle coins between multiple wallets, making the trail almost impossible to follow. This is one of the fastest-growing trends in laundering, especially as crypto adoption increases. Unfortunately, regulation is still playing catch-up in many parts of the world.
Case Insight: In 2024, a big European bank was put on notice to pay a $900 million fine for failing to adequately monitor illegal fund flows, leading to heavy operational and reputational losses.
How to Prevent Money Laundering?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Anti-Money Laundering consists of regulations, laws and procedures aimed at detecting and preventing illicit money flows in financial systems. The actual purpose of AML is to prevent criminal groups from disguising illegally obtained money as legitimate income. Customer due diligence (KYC), transaction monitoring, sanction screening, and the reporting of suspicious activities are essential components of AML. International AML standards are set by some global organizations such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). Local compliance, on the other hand, is provided by regional laws like the USA PATRIOT Act and the EU’s AML Directives. Financial institutions are required to implement robust AML controls to protect themselves from being exploited by money launderers. Overall, AML efforts help safeguard the integrity of global financial systems.
Implementing KYC (Know Your Customer)
Preventing money laundering requires more than regulation - it requires banks, businesses, regulators, and even the public to work together. Every party has a stake in knowing and preventing criminal financial transactions. No one method guarantees success, but employing a mix of best practices reduces the risk of abuse. The most elemental of the instruments is the Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regime. These laws oblige institutions, especially banks, to verify customers' identities before offering financial facilities. Having a bank account alone is not enough; institutions should dig deeper to find out about the person who is, who he or she is receiving funds from, and whether his or her business endeavors seem genuine. This due diligence acts to shut down high-risk individuals or entities from abusing the financial system. While the KYC and AML controls are unlikely to identify all such cases, they are an important first line of defense against criminal penetration.
Transaction Tracking Systems
Another vital approach is adopting clever transaction tracking systems, especially those driven by way of artificial intelligence. These structures reveal economic activity in real time and raise a red flag over any strange or suspicious activity like inconsistent styles of transactions or cross-border transactions that do not healthy a client's profile. From our expert's experience, depending only on manual review in the speedy-paced international of nowadays is not an option. AI tools are not only useful - they're indispensable. They allow compliance teams to move quickly before suspicious transactions go through undetected.
Trainings for Employee Awareness
Finally, as important as systems and technology are, we cannot eliminate the human touch. Employee awareness and training programs ensure that employees are aware of how to see red flags and respond appropriately. Technology can highlight exceptions, yet it is on people to contextualize warnings, follow up leads, and apply good judgment calls. When companies invest in continually updated training, they foster responsibility and vigilance. That cultural shift - when every employee feels responsible for protecting the organization - can be the key to keeping financial crimes at bay.
Key AML Regulations and Laws Against Money Laundering
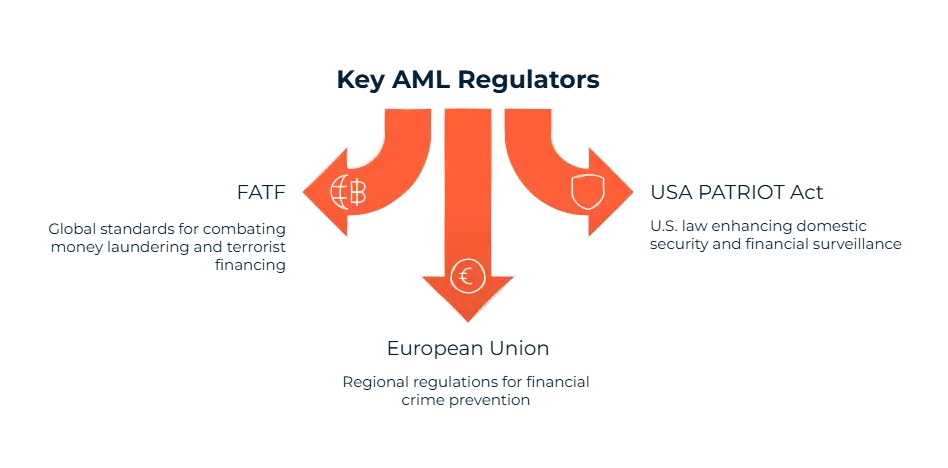
FATF Recommendations: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets globally recognized standards while combating money laundering. Recommendation 10 (Customer Due Diligence) confirms customer identities and tracks their transactions. Recommendation 20 (Suspicious Transaction Reporting) reports unusual activity. Thus, FATF Recommendations become inevitable to provide transparency in financial systems.
EU 6AMLD: Building upon FATF Recommendations, the European Union’s 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) strengthens the legal framework. It is a directive that introduces a list of 22 offences, including cybercrime and environmental crime. EU 6AMLD will prove to be a liability for companies across EU member states.
U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA): It is required by the U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) that financial institutions must implement monitoring systems for suspicious activities. Institutions must file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) and Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs) under the supervision of FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network).
What Are the Examples of Money Laundering?
Money laundering is not just a white-collar crime. It helps to promote global instability. Criminals traffic trillions annually, utilizing banks, shell companies, and internet networks to fund terror, corruption, and organized crime.
Looking at some high-profile cases gives insight. In 2012, HSBC admitted to allowing Mexican drug cartels to launder hundreds of millions of dollars through its banks. The bank failed to report obvious red flags and even modified systems to speed up suspicious transactions. For this, they paid a $1.9 billion fine. Critics argued that the exceptional becomes slightly a slap at the wrist in comparison to the damage carried out, however.
Danske Bank was embroiled in a big scandal while investigators located over €200 billion in suspicious transactions via its Estonian branch. Most of that money came from Russian and Eastern European foundations, and the financial institution didn't ask too many questions. The affair exposed serious weaknesses in banking oversight and compliance.
Cryptocurrency has attracted a new type of criminal. Scams involving faux NFT projects and preliminary coin offerings (ICOs) are actually commonplace. One method is to apply Bitcoin "mixers" to cover the origin of stolen or unlawful funds. It's a reminder that economic crime evolves with technology, and rapidly.
| Type of Money Laundering | Example | Sector Involved | Red Flags |
| Smurfing (Structuring) | $100,000 split into multiple deposits under $10,000 to avoid reporting | Banking | Multiple small cash deposits, different branches, unusual timing |
| Trade-Based Laundering | Over-invoicing imported goods to transfer value | Import/Export | Invoice mismatch, goods mispricing, high-value low-weight items |
| Real Estate Laundering | Buying properties with illicit funds, later selling to legitimize the money | Real Estate | All-cash purchases, below/above market value deals, rapid reselling |
| Casino-Based Laundering | Buying chips with dirty money, playing a little, then cashing out as "winnings" | Gambling | High chip purchases, low play activity, quick cash-outs |
| Shell Companies & Trusts | Using offshore companies to disguise ownership and the source of funds | Corporate/Offshore | No clear business purpose, complex structures, and secrecy jurisdictions |
| Digital Currency Laundering | Moving illicit funds through crypto mixers and privacy coins | Crypto / Fintech | Large volume transactions, anonymized addresses, and use of mixing services |
| Invoice Manipulation | Creating fake invoices for non-existent services to move money | B2B Services / Consulting | No delivery proof, repeated payments to new vendors |
| Loan-Back Schemes | Criminal gives funds to an associate who returns it as a "loan repayment" | Personal / SME Lending | Loan with no terms, no collateral, and no actual repayment schedule |
| Cash-Intensive Businesses | Laundering funds through businesses like car washes or restaurants | Retail / Services | Unusual cash volume, inconsistent with industry norms |
| Charity Laundering | Funnel money through a fake nonprofit or NGO | Nonprofit Sector | Lack of real operations, large unexplained donations, offshore connections |
Statistics of Money Laundering (Updated for 2025)
• Criminals Launder Up to $2 Trillion Each Year
According to UNODC, illicit parties move $800 billion to $2 trillion annually, which is nearly 5% of global GDP.
• Banks Facilitate 70% of Laundering Cases
Financial institutions are used by criminals to launder proceeds, exposing banks to massive regulatory and reputational chance.
• Cybercriminals Moved $23.8 Billion through Online Channels in 2024
With the upward push of crypto scams and online fraud, money launderers now make use of online structures greater than ever (FBI IC3).
• EU Banks Fined €4 Billion by Regulators for AML Shortcomings in 2023
Regulators imposed a high level of fines on European banks that did not observe anti-money laundering guidelines.
• 10% of High-Net-Worth Individuals Are Involved in Suspicious Transactions
One in ten high-net-worth individuals used belongings, art, or luxurious goods to move or cover suspicious price ranges.
What’s New in Money Laundering Trends in 2025?
In 2025, global regulators have raised the stakes. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) now recommends real-time KYC checks and AI-based monitoring. Europol's latest report threatens money laundering fueled by crypto, and FinCEN in the US has expanded regulations requiring businesses to disclose ultimate beneficial owners. These changes aim to expose dirty business and hold financial institutions accountable. And as the world works together, cross-border money laundering could become increasingly hard to carry out.
How Sanction Scanner Helps You About Anti Money Laundering?
We are at the forefront with innovative technology to fight this global issue. We believe that technology is the only way in which we can keep pace with the constantly evolving scams used by financial scoundrels. Sanction Scanner offers real-time, AI-powered AML solutions that look to identify early and constantly monitor. Our most valuable asset must be their sanction and watchlist screen capability. It screens people and entities against more than 3,000 global databases, flagging high-risk profiles at onboarding. This preventive approach can prevent suspicious parties from even reaching the system in the first place.
Our platform also provides continuous risk monitoring. When the risk profile of a customer shifts—e.g., is sanctioned or deemed a politically exposed person (PEP)—the system instantly sends a message to the compliance officers. This permits agencies to react quicker in preference of performing too slowly. The different critical element is synthetic intelligence-powered transactional tracking. Instead of counting on inflexible guidelines, the machine develops insight primarily based on patterns of conduct. It spots outliers like velocity transfers or structuring and issues warnings for human beings to review. For us, this is the region wherein AI honestly shines through, permitting groups to hone in on authentic risks without getting mired in fake positives.
Negative media screening is another excellent added layer of protection. By searching online news and media for negative press, our product offers context that can't be offered by databases. If someone isn't officially sanctioned but does have serious accusations in the media, businesses are still able to make educated business decisions.
FAQ's Blog Post
Money laundering is the process of making illegally obtained money appear legal. It involves three stages: placement, layering, and integration.
AML refers to regulations and practices designed to prevent criminals from disguising illegal funds. It includes KYC, transaction monitoring, and SAR filing.
Penalties vary globally but often include fines, imprisonment (up to 20 years in the U.S.), and asset confiscation.
Warning signs include large unexplained transactions, use of shell companies, and reluctance to share financial details.
There's no fixed threshold, but suspicious amounts—especially just under $10,000—can trigger reporting obligations or investigations.
Through suspicious activity monitoring, structuring detection, and automated AML software that flags abnormal behavior.
Placement (inserting illicit funds), Layering (obscuring their origin), and Integration (reintroducing as clean money).
Shell companies, trade-based laundering, real estate, gambling, and cryptocurrency mixers are frequently used.
Agencies like FinCEN (U.S.), FCA (UK), and Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs) in various countries handle investigations.
It enables further crimes like terrorism and human trafficking, harms economies, and undermines the integrity of financial systems.


